| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Convert degrees to radians.
In this example, we start with degrees and want radians, so we again set up a proportion, but we substitute the given information into a different part of the proportion.
Converting between degrees and radians can make working with angles easier in some applications. For other applications, we may need another type of conversion. Negative angles and angles greater than a full revolution are more awkward to work with than those in the range of to or to It would be convenient to replace those out-of-range angles with a corresponding angle within the range of a single revolution.
It is possible for more than one angle to have the same terminal side. Look at [link] . The angle of is a positive angle, measured counterclockwise. The angle of is a negative angle, measured clockwise. But both angles have the same terminal side. If two angles in standard position have the same terminal side, they are coterminal angles . Every angle greater than or less than is coterminal with an angle between and and it is often more convenient to find the coterminal angle within the range of to than to work with an angle that is outside that range.
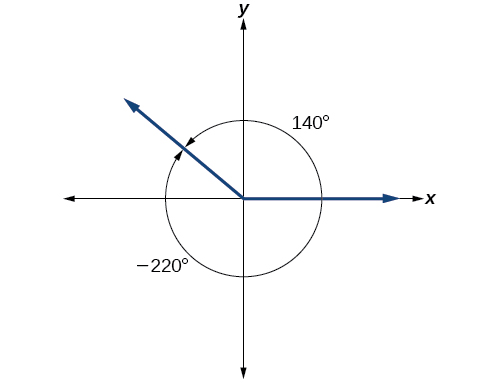
Any angle has infinitely many coterminal angles because each time we add to that angle—or subtract from it—the resulting value has a terminal side in the same location. For example, and are coterminal for this reason, as is
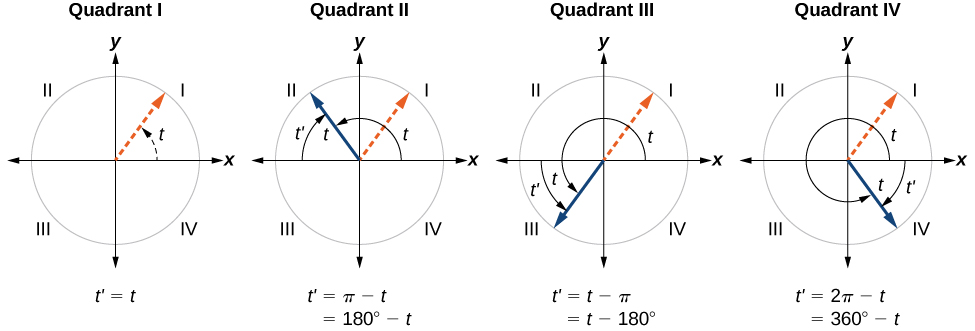
An angle’s reference angle is the measure of the smallest, positive, acute angle formed by the terminal side of the angle and the horizontal axis. Thus positive reference angles have terminal sides that lie in the first quadrant and can be used as models for angles in other quadrants. See [link] for examples of reference angles for angles in different quadrants.
Coterminal angles are two angles in standard position that have the same terminal side.
An angle’s reference angle is the size of the smallest acute angle, formed by the terminal side of the angle and the horizontal axis.
Given an angle greater than find a coterminal angle between and
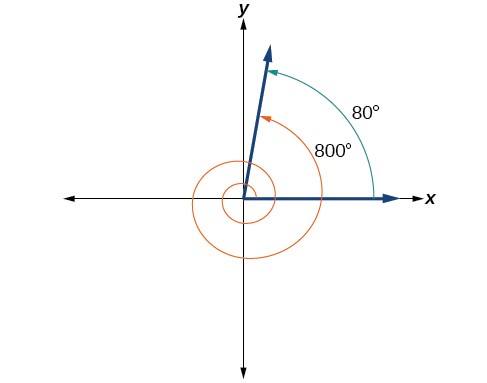
Find the least positive angle that is coterminal with an angle measuring where
An angle with measure is coterminal with an angle with measure but is still greater than so we subtract again to find another coterminal angle:
The angle is coterminal with To put it another way, equals plus two full rotations, as shown in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?