| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Bipolar disorder is considerably less frequent than major depressive disorder. In the United States, 1 out of every 167 people meets the criteria for bipolar disorder each year, and 1 out of 100 meet the criteria within their lifetime (Merikangas et al., 2011). The rates are higher in men than in women, and about half of those with this disorder report onset before the age of 25 (Merikangas et al., 2011). Around 90% of those with bipolar disorder have a comorbid disorder, most often an anxiety disorder or a substance abuse problem. Unfortunately, close to half of the people suffering from bipolar disorder do not receive treatment (Merikangas&Tohen, 2011). Suicide rates are extremely high among those with bipolar disorder: around 36% of individuals with this disorder attempt suicide at least once in their lifetime (Novick, Swartz,&Frank, 2010), and between 15%–19% complete suicide (Newman, 2004).
Mood disorders have been shown to have a strong genetic and biological basis. Relatives of those with major depressive disorder have double the risk of developing major depressive disorder, whereas relatives of patients with bipolar disorder have over nine times the risk (Merikangas et al., 2011). The rate of concordance for major depressive disorder is higher among identical twins than fraternal twins (50% vs. 38%, respectively), as is that of bipolar disorder (67% vs. 16%, respectively), suggesting that genetic factors play a stronger role in bipolar disorder than in major depressive disorder (Merikangas et al. 2011).
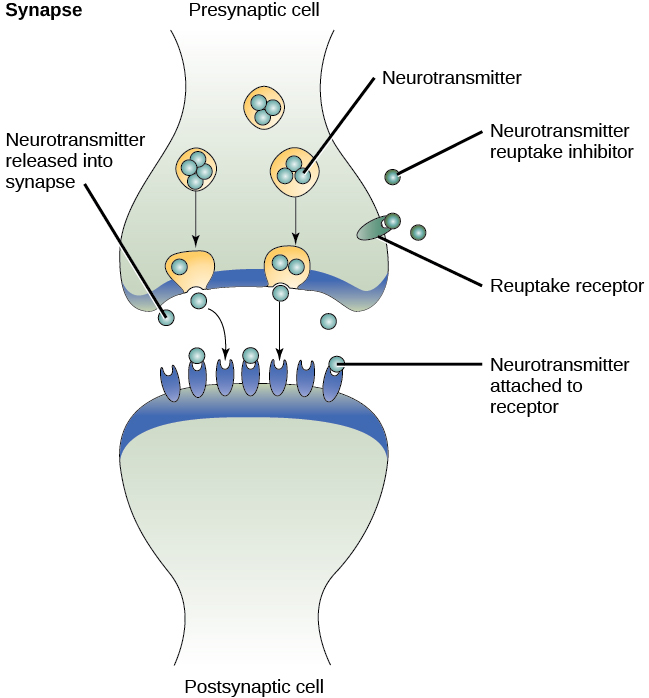
People with mood disorders often have imbalances in certain neurotransmitters, particularly norepinephrine and serotonin (Thase, 2009). These neurotransmitters are important regulators of the bodily functions that are disrupted in mood disorders, including appetite, sex drive, sleep, arousal, and mood. Medications that are used to treat major depressive disorder typically boost serotonin and norepinephrine activity, whereas lithium—used in the treatment of bipolar disorder—blocks norepinephrine activity at the synapses ( [link] ).
Depression is linked to abnormal activity in several regions of the brain (Fitzgerald, Laird, Maller,&Daskalakis, 2008) including those important in assessing the emotional significance of stimuli and experiencing emotions (amygdala), and in regulating and controlling emotions (like the prefrontal cortex, or PFC) (LeMoult, Castonguay, Joormann,&McAleavey, 2013). Depressed individuals show elevated amygdala activity (Drevets, Bogers,&Raichle, 2002), especially when presented with negative emotional stimuli, such as photos of sad faces ( [link] ) (Surguladze et al., 2005). Interestingly, heightened amygdala activation to negative emotional stimuli among depressed persons occurs even when stimuli are presented outside of conscious awareness (Victor, Furey, Fromm, Öhman,&Drevets, 2010), and it persists even after the negative emotional stimuli are no longer present (Siegle, Thompson, Carter, Steinhauer,&Thase, 2007). Additionally, depressed individuals exhibit less activation in the prefrontal, particularly on the left side (Davidson, Pizzagalli,&Nitschke, 2009). Because the PFC can dampen amygdala activation, thereby enabling one to suppress negative emotions (Phan et al., 2005), decreased activation in certain regions of the PFC may inhibit its ability to override negative emotions that might then lead to more negative mood states (Davidson et al., 2009). These findings suggest that depressed persons are more prone to react to emotionally negative stimuli, yet have greater difficulty controlling these reactions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?