| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
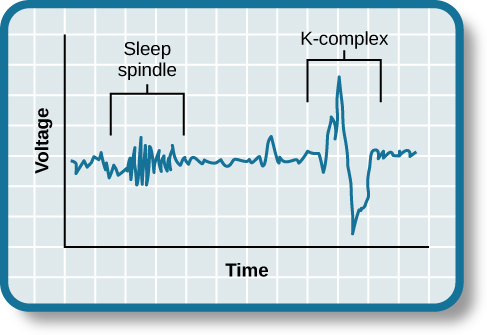
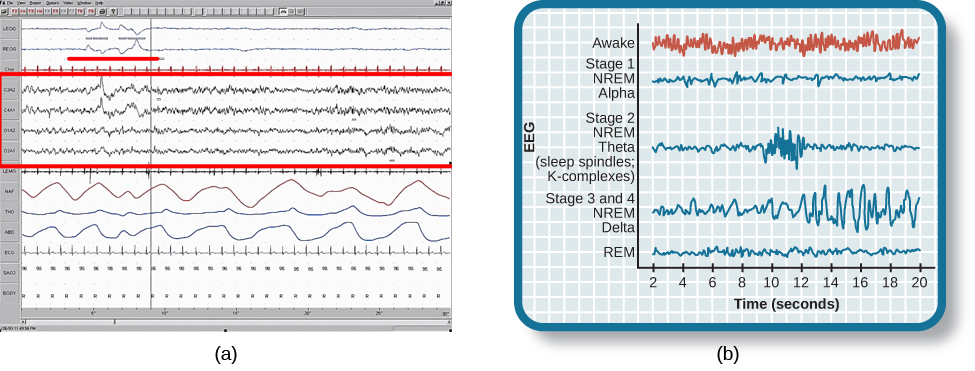
Stage 3 and stage 4 of sleep are often referred to as deep sleep or slow-wave sleep because these stages are characterized by low frequency (up to 4 Hz), high amplitude delta waves ( [link] ). During this time, an individual’s heart rate and respiration slow dramatically. It is much more difficult to awaken someone from sleep during stage 3 and stage 4 than during earlier stages. Interestingly, individuals who have increased levels of alpha brain wave activity (more often associated with wakefulness and transition into stage 1 sleep) during stage 3 and stage 4 often report that they do not feel refreshed upon waking, regardless of how long they slept (Stone, Taylor, McCrae, Kalsekar,&Lichstein, 2008).

As mentioned earlier, REM sleep is marked by rapid movements of the eyes. The brain waves associated with this stage of sleep are very similar to those observed when a person is awake, as shown in [link] , and this is the period of sleep in which dreaming occurs. It is also associated with paralysis of muscle systems in the body with the exception of those that make circulation and respiration possible. Therefore, no movement of voluntary muscles occurs during REM sleep in a normal individual; REM sleep is often referred to as paradoxical sleep because of this combination of high brain activity and lack of muscle tone. Like NREM sleep, REM has been implicated in various aspects of learning and memory (Wagner, Gais,&Born, 2001), although there is disagreement within the scientific community about how important both NREM and REM sleep are for normal learning and memory (Siegel, 2001).
If people are deprived of REM sleep and then allowed to sleep without disturbance, they will spend more time in REM sleep in what would appear to be an effort to recoup the lost time in REM. This is known as the REM rebound, and it suggests that REM sleep is also homeostatically regulated. Aside from the role that REM sleep may play in processes related to learning and memory, REM sleep may also be involved in emotional processing and regulation. In such instances, REM rebound may actually represent an adaptive response to stress in nondepressed individuals by suppressing the emotional salience of aversive events that occurred in wakefulness (Suchecki, Tiba,&Machado, 2012).
While sleep deprivation in general is associated with a number of negative consequences (Brown, 2012), the consequences of REM deprivation appear to be less profound (as discussed in Siegel, 2001). In fact, some have suggested that REM deprivation can actually be beneficial in some circumstances. For instance, REM sleep deprivation has been demonstrated to improve symptoms of people suffering from major depression, and many effective antidepressant medications suppress REM sleep (Riemann, Berger,&Volderholzer, 2001; Vogel, 1975).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?