| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
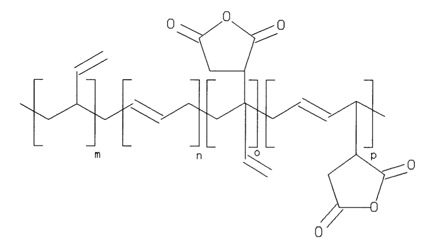
Organic polymer based packing material is not limited by pH like the silica gel materials are, but are not suitable for separation of alkali metals and alkali earth metals. The most common functional group is the sulfonic acid group ( [link] ), attached with a spacer between the polymer and the sulfonic acid group.

Photometric detection in the UV region of the spectrum is a common method of detection in ion chromatography. Photometric methods limit the eluent possibilities, as the analyte must have a unique absorbance wavelength to be detectable. Cations that do not have a unique absorbance wavelength, i.e. the eluent and other contaminants have similar UV visible spectra can be complexed to for UV visible compounds. This allows detection of the cation without interference from eluents.
Coupling the chromatography with various types of spectroscopy such as Mass spectroscopy or IR spectroscopy can be a useful method of detection. Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy is a commonly used method.
Direct conductivity methods take advantage of the change in conductivity that an analyte produces in the eluent, which can be modeled by [link] , where equivalent conductivity is defined as [link] .
With L being the distance between two electrodes of area A and R being the resistance the ion creates. C is the concentration of the ion. The conductivity can be plotted over time, and the peaks that appear represent different ions coming through the column as described by [link] .
The values of Equivalent conductivity of the analyte and of the eluent common ions can be found in [link] .

The choice of eluent depends on many factors, namely, pH, buffer capacity, the concentration of the eluent, and the nature of the eluent’s reaction with the column and the packing material.
In non-suppressed anion chromatography, where the eluent and analyte are not altered between the column and the detector, there is a wide range of eluents to be used. In the non-suppressed case, the only issue that could arise is if the eluent impaired the detection ability (absorbing in a similar place in a UV-spectra as the analyte for instance). As such, there are a number of commonly used eluents. Aromatic carboxylic acids are used in conductivity detection because of their low self-conductivity. Aliphatic carboxylic acids are used for UV/visible detection because they are UV transparent. Inorganic acids can only be used in photometric detection.
In suppressed anion chromatography, where the eluent and analyte are treated between the column and detection, fewer eluents can be used. The suppressor modifies the eluent and the analyte, reducing the self-conductivity of the eluent and possibly increasing the self-conductivity of the analyte. Only alkali hydroxides and carbonates, borates, hydrogen carbonates, and amino acids can be used as eluents.
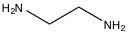
The primary eluents used in cation chromatography of alkali metals and ammoniums are mineral acids such as HNO 3 . When the cation is multivalent, organic bases such as ethylenediamine ( [link] ) serve as the main eluents. If both alkali metals and alkali earth metals are present, hydrochloric acid or 2,3-diaminopropionic acid ( [link] ) is used in combination with a pH variation. If the chromatography is unsuppressed, the direct conductivity measurement of the analyte will show up as a negative peak due to the high conductivity of the H + in the eluent, but simple inversion of the data can be used to rectify this discrepancy.

If transition metals or H + are the analytes in question, complexing carboxylic acids are used to suppress the charge of the analyte and to create photometrically detectable complexes, forgoing the need for direct conductivity as the detection method.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?