| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A circuit element dissipates or produces power according to where I is the current through the element and V is the voltage across it. Since the current and the voltage both depend on time in an ac circuit, the instantaneous power is also time dependent. A plot of p ( t ) for various circuit elements is shown in [link] . For a resistor, i ( t ) and v ( t ) are in phase and therefore always have the same sign (see [link] ). For a capacitor or inductor, the relative signs of i ( t ) and v ( t ) vary over a cycle due to their phase differences (see [link] and [link] ). Consequently, p ( t ) is positive at some times and negative at others, indicating that capacitive and inductive elements produce power at some instants and absorb it at others.
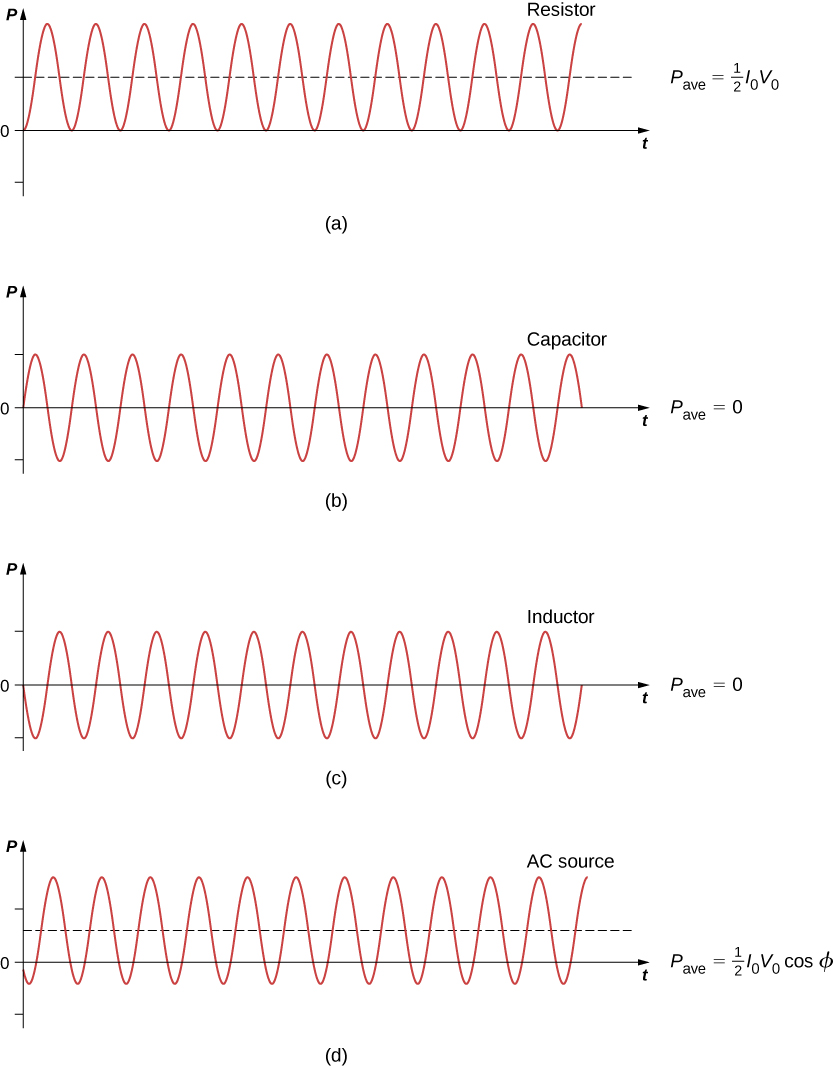
Because instantaneous power varies in both magnitude and sign over a cycle, it seldom has any practical importance. What we’re almost always concerned with is the power averaged over time, which we refer to as the average power . It is defined by the time average of the instantaneous power over one cycle:
where is the period of the oscillations. With the substitutions and this integral becomes
Using the trigonometric relation we obtain
Evaluation of these two integrals yields
and
Hence, the average power associated with a circuit element is given by
In engineering applications, is known as the power factor , which is the amount by which the power delivered in the circuit is less than the theoretical maximum of the circuit due to voltage and current being out of phase. For a resistor, so the average power dissipated is
A comparison of p ( t ) and is shown in [link] (d). To make look like its dc counterpart, we use the rms values of the current and the voltage. By definition, these are
where
With we obtain
We may then write for the average power dissipated by a resistor,
This equation further emphasizes why the rms value is chosen in discussion rather than peak values. Both equations for average power are correct for [link] , but the rms values in the formula give a cleaner representation, so the extra factor of 1/2 is not necessary.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?