| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In the preceding section, we defined the moment of inertia but did not show how to calculate it. In this section, we show how to calculate the moment of inertia for several standard types of objects, as well as how to use known moments of inertia to find the moment of inertia for a shifted axis or for a compound object. This section is very useful for seeing how to apply a general equation to complex objects (a skill that is critical for more advanced physics and engineering courses).
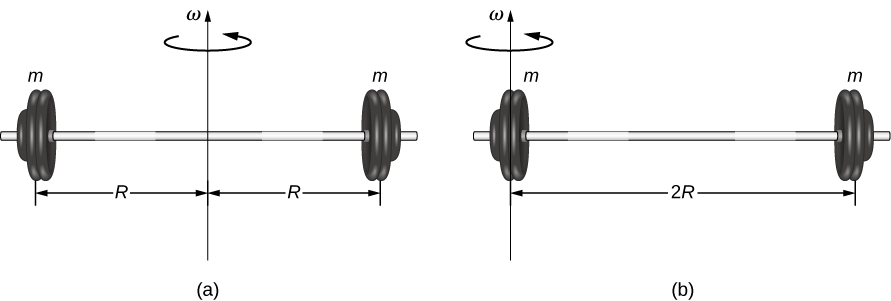
We defined the moment of inertia I of an object to be for all the point masses that make up the object. Because r is the distance to the axis of rotation from each piece of mass that makes up the object, the moment of inertia for any object depends on the chosen axis. To see this, let’s take a simple example of two masses at the end of a massless (negligibly small mass) rod ( [link] ) and calculate the moment of inertia about two different axes. In this case, the summation over the masses is simple because the two masses at the end of the barbell can be approximated as point masses, and the sum therefore has only two terms.
In the case with the axis in the center of the barbell, each of the two masses m is a distance R away from the axis, giving a moment of inertia of
In the case with the axis at the end of the barbell—passing through one of the masses—the moment of inertia is
From this result, we can conclude that it is twice as hard to rotate the barbell about the end than about its center.
In this example, we had two point masses and the sum was simple to calculate. However, to deal with objects that are not point-like, we need to think carefully about each of the terms in the equation. The equation asks us to sum over each ‘piece of mass’ a certain distance from the axis of rotation. But what exactly does each ‘piece of mass’ mean? Recall that in our derivation of this equation, each piece of mass had the same magnitude of velocity, which means the whole piece had to have a single distance r to the axis of rotation. However, this is not possible unless we take an infinitesimally small piece of mass dm , as shown in [link] .
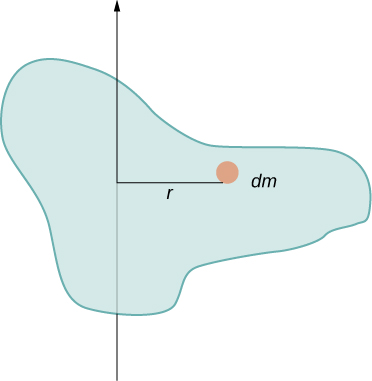
The need to use an infinitesimally small piece of mass dm suggests that we can write the moment of inertia by evaluating an integral over infinitesimal masses rather than doing a discrete sum over finite masses:
This, in fact, is the form we need to generalize the equation for complex shapes. It is best to work out specific examples in detail to get a feel for how to calculate the moment of inertia for specific shapes. This is the focus of most of the rest of this section.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?