| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
where is the average band edge and is half the transition band width in radians per second normalized for one sample persecond sampling rate [link] , [link] , [link] . The spline produces a transition function which consists of segments of order polynomials connected together so that derivatives are continuous at the junctions.
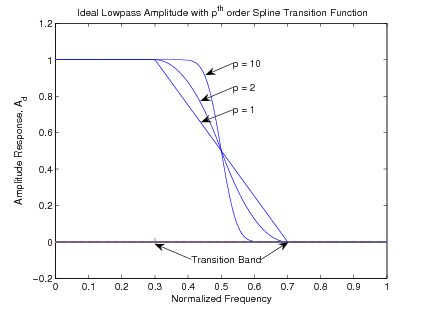
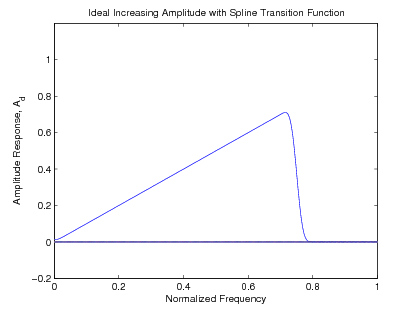
The optimal value of the exponent is chosen as (for a unity sampling rate) which minimizes the approximation error [link] . Each of the four ideal lowpass filters derived in the previous can have a transition band addedsimply by multiplying their impulse response by the sinc weighting function as illustrated in [link] . [link] shows an ideal unity gain filter amplitude response with examples of first,second, and tenth order spline transition functions. [link] shows the ideal responses of the linear gain filter with fourth order spline transition function.
The optimal multiband design method consists of two somewhat independent parts. The first is the design of an optimal least squares lowpass filterwith a transition band as described above or as calculated by an inverse FFT. The second part builds an optimal multiband filter from acombination of these optimal lowpass filters and is the main point of this [link] .
The unweighted least squared error linear phase FIR filter design problem is to find the filter coefficients that minimize the error defined by
where is the amplitude frequency response of the actual filter and is the desired ideal amplitude response. This is done by truncating the inverse discrete time Fourier transform of . The difficulty is the analytical evaluation of the integral in the inverse transform [link] . If a spline transition function is used, an analytical formula can be derived for the filter thatminimizes [link] . The details of this result can be found in [link] , [link] .
The infinitely long filters designed from the inverse discrete time Fourier transform of the ideal response have a frequency response which isthe same as the ideal and, therefore, has no error. An ideal desired amplitude response can be formulated as the sum of simpler ideal lowpassfilters, differentiators or Hilbert transformers together with their spline transition functions by
where is the desired lowpass response with a transition band in the band such as given in [link] or [link] and the are chosen to build the desired . These are the forms considered in the previous section along with any others that have analytical inverse DTFTs such as polynomials. Because of thelinearity of the Fourier transform, a multiband ideal response can be constructed by simply adding and subtracting the impulse response ofappropriate ideal lowpass filters.
Because of the orthogonality of the basis functions of the Fourier transform, the truncated sequence of the infinitely long impulse response will give an optimal approximation to in a least squares sense. This argument allows no error weighting or “don'tcare" transition bands or traditional windowing methods. It does, however, allow the optimized spline transition functions [link] , [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Digital signal processing and digital filter design (draft)' conversation and receive update notifications?