| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Nội trở của nối tại điểm Q là:
Khi nối P-N phân cực thuận càng mạnh, dòng điện I càng lớn trong lúc điện thế V gần như không đổi nên nội trở càng nhỏ.
Giả sử dòng dòng điện ngang qua nối P-N là IQ tương ứng với một điện thế phân cực thuận VQ.
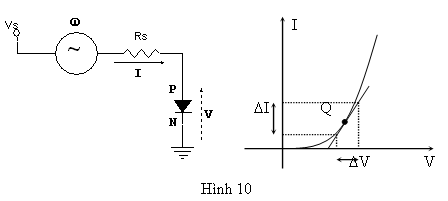
Khi V biến thiên một lượng V từ trị số VQ thì I cũng biến thiên một lượng tương ứng I từ trị số IQ. Tỉ số bằng với độ dốc của tiếp tuyến tại điểm Q với đặc tuyến của nối P-N.
Đặt: ;rd được gọi là điện trở động của nối P-N khi phân cực thuận.
Với tín hiệu u nhỏ, ta có:
Với
Suy ra:
Ngoài ra,
Hay
Do đó,
Và điện trở động là:
Thông thường, nên
Ở nhiệt độ bình thường (250C), VT = 26mV, điện trở động là:
Với dòng điện I khá lớn, =1, điện trở động rd có thể được tính theo công thức:
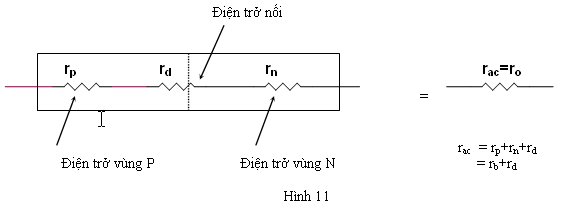
Ở nhiệt độ bình thường, nếu IQ = 100mA thì rd = 0,26. Trong một nối P-N thực, vì có tiếp trở giữa các mối nối, điện trở giữa hai vùng bán dẫn P và N nên điện trở động thực sự lớn hơn nhiều so với trị số tính được, thông thường khoảng vài chục .
Đây cũng chính là kiểu mẫu của Diode với tín hiệu nhỏ. Người ta cũng định nghĩa điện trở động khi phân cực nghịch
Vì độ dốc của tiếp tuyến tại Q khi nối P-N phân cực nghịch rất nhỏ nên điện trở động rr rất lớn, hàng M.
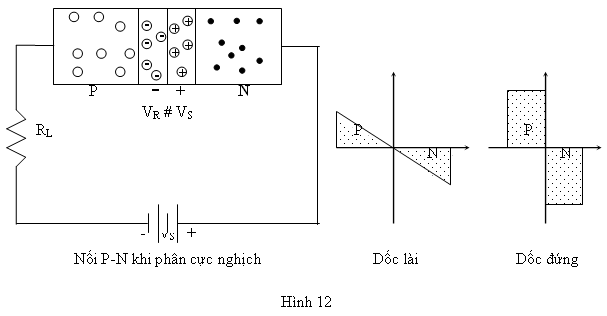
Khi nối P-N được phân cực nghịch, vùng hiếm được nới rộng do có sự gia tăng điện tích trong vùng này. Với một sự biến thiên V của hiệu điện thế phân cực nghịch, điện tích trong vùng hiếm tăng một lượng Q. Vùng hiếm có tác dụng như một tụ điện gọi là điện dung chuyển tiếp CT.
Trong đó, là hằng số điện môi của chất bán dẫn, A là điện tích của nối P-N và Wd là độ rộng của vùng hiếm.
Khi điện thế phân cực nghịch thay đổi, độ rộng của vùng hiếm thay đổi nên điện dung chuyển tiếp CT cũng thay đổi. Người ta chứng minh được CT có trị số:
Trong đó, K là hằng số tùy thuộc vào chất bán dẫn và kỹ thuật chế tạo. V0 là rào điện thế của nối P-N (Si là 0,7V và Ge là 0,3V). VR là điện thế phân cực nghịch. trong trường hợp nối P-N là dốc lài (linearly graded juntion) và trong trường hợp nối P-N thuộc loại dốc đứng (brupt juntion).
Nếu gọi Cj(0) là trị số của CT đo được khi VR=0, ta có:
Trong các nối P-N thông thường, CT có trị số từ 5pF đến 100pF
Khi nối P-N được phân cực thuận, lỗ trống được khuếch tán từ vùng P sang vùng N và điện tử khuếch tán từ vùng N sang vùng P. Sự phân bố các hạt tải điện thiểu số ở hai bên vùng hiếm tạo nên một điện dung gọi là điện dung khuếch tán CD.. Người ta chứng minh được điện dung khuếch tán CDtỉ lệ với dòng điện qua nối P-N theo công thức:
Trong đó, , là đời sống trung bình của lỗ trống; = 2 đối với nối P-N là Si, =1 đối với nối P-N là Ge.
Thông thường, CD có trị số từ 2000pF đến 15000pF.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mạch điện tử' conversation and receive update notifications?