| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Find all the factors of
Divide
by each of the counting numbers starting with
If the quotient is a whole number, the divisor and quotient are a pair of factors.
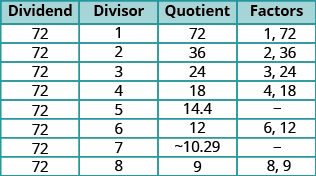
The next line would have a divisor of and a quotient of The quotient would be smaller than the divisor, so we stop. If we continued, we would end up only listing the same factors again in reverse order. Listing all the factors from smallest to greatest, we have
Find all the factors of the given number:
1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 24, 32, 48, 96
Find all the factors of the given number:
1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 16, 20, 40, 80
Some numbers, like have many factors. Other numbers, such as have only two factors: and the number. A number with only two factors is called a prime number . A number with more than two factors is called a composite number . The number is neither prime nor composite. It has only one factor, itself.
A prime number is a counting number greater than whose only factors are and itself.
A composite number is a counting number that is not prime.
[link] lists the counting numbers from through along with their factors. The highlighted numbers are prime, since each has only two factors.
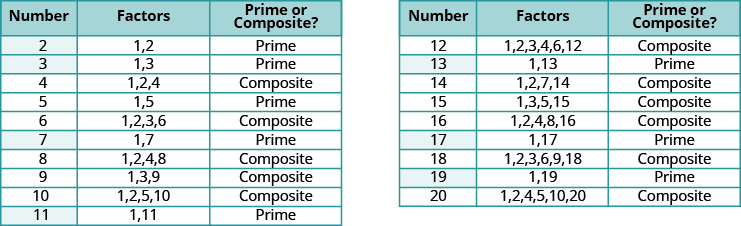
The prime numbers less than are There are many larger prime numbers too. In order to determine whether a number is prime or composite, we need to see if the number has any factors other than and itself. To do this, we can test each of the smaller prime numbers in order to see if it is a factor of the number. If none of the prime numbers are factors, then that number is also prime.
Identify each number as prime or composite:
ⓐ Test each prime, in order, to see if it is a factor of by each of the prime numbers, starting with as shown. We will stop when the quotient is smaller than the divisor.
| Prime | Test | Factor of |
|---|---|---|
| Last digit of is not | No. | |
| and is not divisible by | No. | |
| The last digit of is not or | No. | |
| No. | ||
| No. |
We can stop when we get to because the quotient is less than the divisor.
We did not find any prime numbers that are factors of so we know is prime.
ⓑ Test each prime, in order, to see if it is a factor of
| Prime | Test | Factor of |
|---|---|---|
| Last digit is not | No. | |
| and is not divisible by | No. | |
| the last digit is not or | No. | |
| Yes. |
Since is divisible by we know it is not a prime number. It is composite.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Prealgebra' conversation and receive update notifications?