| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Finally, in selected cases, magnesium will react with acidic hydrocarbons such as cyclopentadienyl at high temperatures (600 °C).
In the vapor phase dialkyl magnesium compounds are generally monomeric linear compounds. In solution, in the absence of coordinating solvents R 2 Mg form a variety of oligomers ( [link] a-c) in solution as determined by molecular weight measurements. In the presence of coordinating solvents 4-coordinate monomers predominate ( [link] d).

As similar trend is observed in the solid state, where polymers have been characterized in the absence of coordinating solvents ( [link] a), while monomers or dimmers are generally observed when crystallized from a coordinating solvent ( [link] b and c).

Grignard compounds react with water to give the hydrocarbon, [link] , they also react with other hydroxylic compounds such as alcohols and carboxylic acids. One important use of the hydrolysis reaction is specifically deuteration, [link] .
The hydrogen atom on a terminal alkyne is sufficiently acidic that the reaction with Grignards occurs in an analogous manner to that of hydrolysis.
Once formed the alkynyl Grignard undergoes the same hydrolysis reaction.
Grignards react readily with carbon dioxide to form the carboxylate, which yields the associated carboxylic acid upon hydrolysis, [link] .
Organomagnesium compounds react with organic carbonyls (aldehydes, ketones, and esters) to yield the alcohol on hydrolysis, [link] . This synthetic route is useful for the formation of primary, secondary and terminal alcohols.
Unfortunately, for some carbonyls there is a competing side reaction of enolization, where the starting ketone is reformed upon hydrolysis.

When the Grignard reagent has a β-hydrogen another side reaction occurs in which the carbonyl group is reduced and an alkene is formed.
Both the enolization and reduction occur via similar 6-membered cyclic transition states ( [link] ).

Grignards react with α,β-unsaturated ketones to give either the 1,2-addition product or the 1,4-addition product, or both.
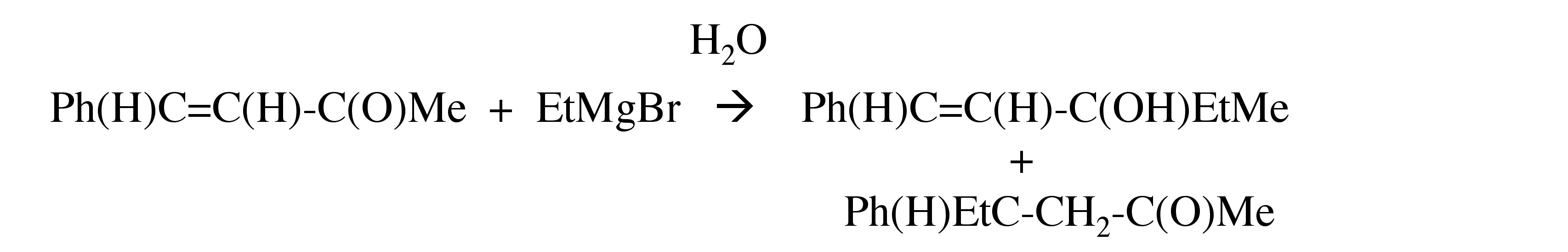
Acyl halides react with Grignards to give ketones, [link] . Best results are obtained if the reaction is carried out at low temperature and in the presence of a Lewis acid catalysts (e.g., FeCl 3 ).
Oxirane (epoxide) rings are opened by Grignards, [link] , in a useful reaction that extends the carbon chain of the Grignard by two carbon atoms. This reaction is best performed with ethylene oxide since the magnesium halide formed is a Lewis acid catalyst for further reactions in the case of substituted oxiranes.

One of the most useful methods of preparing organometallic compounds is the exchange reaction of one organometallic compound with a salt of a different metal, [link] . This is an equilibrium process, whose equilibrium constant is defined by the reduction potential of both metals. In general the reaction will proceed so that the more electropositive metal will form the more ionic salt (usually chloride).
Grignard reagents are particularly useful in this regard, and may be used to prepare a wide range of organometallic compounds. For example:
The reaction with a Grignard is milder than the analogous reaction with lithium reagents, and leads to a lower incident of side-products.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of the main group elements' conversation and receive update notifications?