| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Ribonucleic acid, or RNA, is mainly involved in the process of protein synthesis under the direction of DNA. RNA is usually single-stranded and is made of ribonucleotides that are linked by phosphodiester bonds. A ribonucleotide in the RNA chain contains ribose (the pentose sugar), one of the four nitrogenous bases (A, U, G, and C), and the phosphate group.
There are four major types of RNA: messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and microRNA (miRNA). The first, mRNA, carries the message from DNA, which controls all of the cellular activities in a cell. If a cell requires a certain protein to be synthesized, the gene for this product is turned “on” and the messenger RNA is synthesized in the nucleus. The RNA base sequence is complementary to the coding sequence of the DNA from which it has been copied. However, in RNA, the base T is absent and U is present instead. If the DNA strand has a sequence AATTGCGC, the sequence of the complementary RNA is UUAACGCG. In the cytoplasm, the mRNA interacts with ribosomes and other cellular machinery ( [link] ).
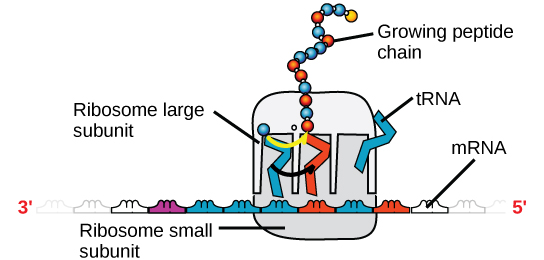
The mRNA is read in sets of three bases known as codons. Each codon codes for a single amino acid. In this way, the mRNA is read and the protein product is made. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a major constituent of ribosomes on which the mRNA binds. The rRNA ensures the proper alignment of the mRNA and the ribosomes; the rRNA of the ribosome also has an enzymatic activity (peptidyl transferase) and catalyzes the formation of the peptide bonds between two aligned amino acids. Transfer RNA (tRNA) is one of the smallest of the four types of RNA, usually 70–90 nucleotides long. It carries the correct amino acid to the site of protein synthesis. It is the base pairing between the tRNA and mRNA that allows for the correct amino acid to be inserted in the polypeptide chain. microRNAs are the smallest RNA molecules and their role involves the regulation of gene expression by interfering with the expression of certain mRNA messages. [link] summarizes features of DNA and RNA.
| Features of DNA and RNA | ||
|---|---|---|
| DNA | RNA | |
| Function | Carries genetic information | Involved in protein synthesis |
| Location | Remains in the nucleus | Leaves the nucleus |
| Structure | Double helix | Usually single-stranded |
| Sugar | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
| Pyrimidines | Cytosine, thymine | Cytosine, uracil |
| Purines | Adenine, guanine | Adenine, guanine |
Even though the RNA is single stranded, most RNA types show extensive intramolecular base pairing between complementary sequences, creating a predictable three-dimensional structure essential for their function.
As you have learned, information flow in an organism takes place from DNA to RNA to protein. DNA dictates the structure of mRNA in a process known as transcription , and RNA dictates the structure of protein in a process known as translation . This is known as the Central Dogma of Life, which holds true for all organisms; however, exceptions to the rule occur in connection with viral infections.
To learn more about DNA, explore the Howard Hughes Medical Institute BioInteractive animations on the topic of DNA.
Nucleic acids are molecules made up of nucleotides that direct cellular activities such as cell division and protein synthesis. Each nucleotide is made up of a pentose sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group. There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA. DNA carries the genetic blueprint of the cell and is passed on from parents to offspring (in the form of chromosomes). It has a double-helical structure with the two strands running in opposite directions, connected by hydrogen bonds, and complementary to each other. RNA is single-stranded and is made of a pentose sugar (ribose), a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group. RNA is involved in protein synthesis and its regulation. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is copied from the DNA, is exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, and contains information for the construction of proteins. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a part of the ribosomes at the site of protein synthesis, whereas transfer RNA (tRNA) carries the amino acid to the site of protein synthesis. microRNA regulates the use of mRNA for protein synthesis.
[link] A mutation occurs, and cytosine is replaced with adenine. What impact do you think this will have on the DNA structure?
[link] Adenine is larger than cytosine and will not be able to base pair properly with the guanine on the opposing strand. This will cause the DNA to bulge. DNA repair enzymes may recognize the bulge and replace the incorrect nucleotide.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?