| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
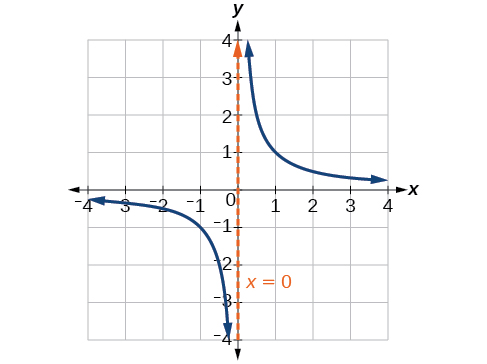
A vertical asymptote of a graph is a vertical line where the graph tends toward positive or negative infinity as the inputs approach We write
As the values of approach infinity, the function values approach 0. As the values of approach negative infinity, the function values approach 0. See [link] . Symbolically, using arrow notation
Based on this overall behavior and the graph, we can see that the function approaches 0 but never actually reaches 0; it seems to level off as the inputs become large. This behavior creates a horizontal asymptote , a horizontal line that the graph approaches as the input increases or decreases without bound. In this case, the graph is approaching the horizontal line See [link] .
A horizontal asymptote of a graph is a horizontal line where the graph approaches the line as the inputs increase or decrease without bound. We write
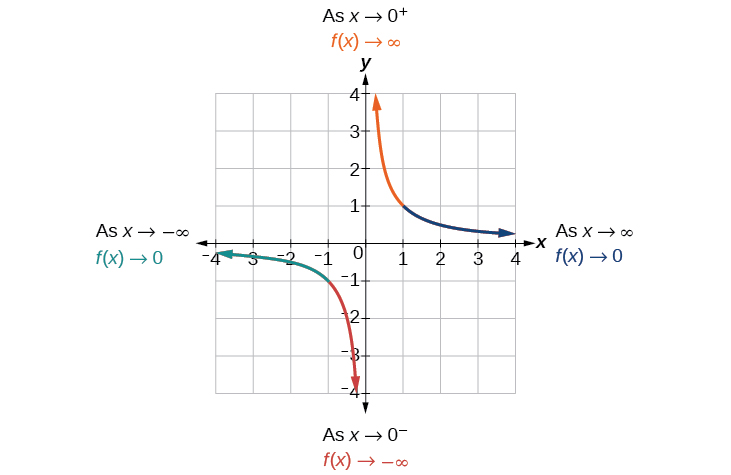
Use arrow notation to describe the end behavior and local behavior of the function graphed in [link] .
Notice that the graph is showing a vertical asymptote at which tells us that the function is undefined at
And as the inputs decrease without bound, the graph appears to be leveling off at output values of 4, indicating a horizontal asymptote at As the inputs increase without bound, the graph levels off at 4.
Use arrow notation to describe the end behavior and local behavior for the reciprocal squared function.
End behavior: as Local behavior: as (there are no x - or y -intercepts)
Sketch a graph of the reciprocal function shifted two units to the left and up three units. Identify the horizontal and vertical asymptotes of the graph, if any.
Shifting the graph left 2 and up 3 would result in the function
or equivalently, by giving the terms a common denominator,
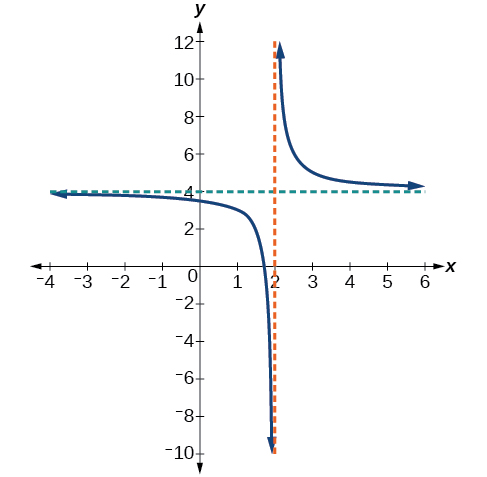
The graph of the shifted function is displayed in [link] .
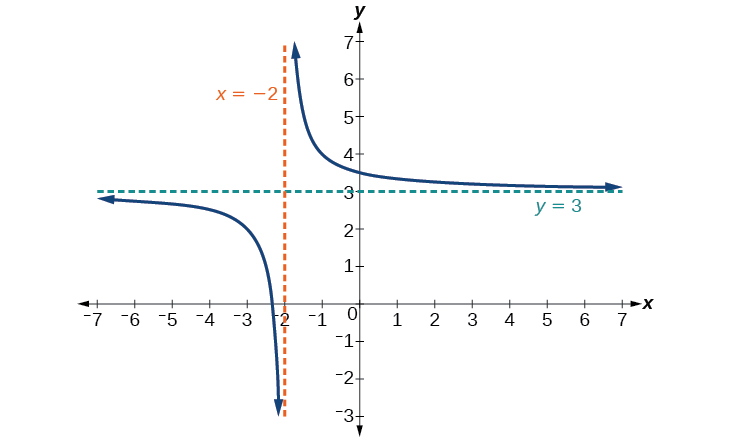
Notice that this function is undefined at and the graph also is showing a vertical asymptote at
As the inputs increase and decrease without bound, the graph appears to be leveling off at output values of 3, indicating a horizontal asymptote at
Sketch the graph, and find the horizontal and vertical asymptotes of the reciprocal squared function that has been shifted right 3 units and down 4 units.
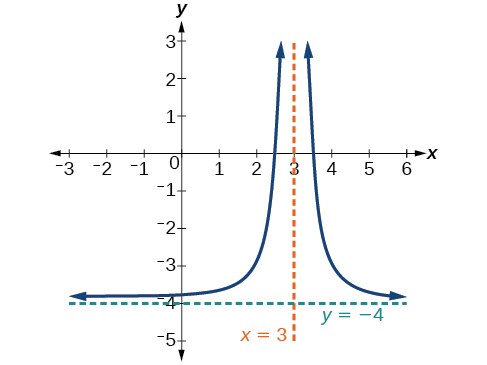
The function and the asymptotes are shifted 3 units right and 4 units down. As and as
The function is
In [link] , we shifted a toolkit function in a way that resulted in the function This is an example of a rational function. A rational function is a function that can be written as the quotient of two polynomial functions. Many real-world problems require us to find the ratio of two polynomial functions. Problems involving rates and concentrations often involve rational functions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?