| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
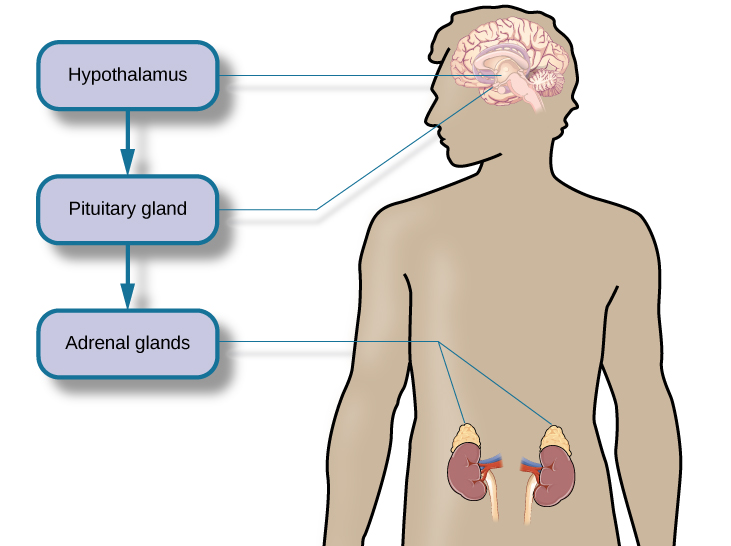
What goes on inside our bodies when we experience stress? The physiological mechanisms of stress are extremely complex, but they generally involve the work of two systems—the sympathetic nervous system and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis . When a person first perceives something as stressful (Selye’s alarm reaction), the sympathetic nervous system triggers arousal via the release of adrenaline from the adrenal glands. Release of these hormones activates the fight-or-flight responses to stress, such as accelerated heart rate and respiration. At the same time, the HPA axis, which is primarily endocrine in nature, becomes especially active, although it works much more slowly than the sympathetic nervous system. In response to stress, the hypothalamus (one of the limbic structures in the brain) releases corticotrophin-releasing factor, a hormone that causes the pituitary gland to release adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) ( [link] ). The ACTH then activates the adrenal glands to secrete a number of hormones into the bloodstream; an important one is cortisol, which can affect virtually every organ within the body. Cortisol is commonly known as a stress hormone and helps provide that boost of energy when we first encounter a stressor, preparing us to run away or fight. However, sustained elevated levels of cortisol weaken the immune system.
In short bursts, this process can have some favorable effects, such as providing extra energy, improving immune system functioning temporarily, and decreasing pain sensitivity. However, extended release of cortisol—as would happen with prolonged or chronic stress—often comes at a high price. High levels of cortisol have been shown to produce a number of harmful effects. For example, increases in cortisol can significantly weaken our immune system (Glaser&Kiecolt-Glaser, 2005), and high levels are frequently observed among depressed individuals (Geoffroy, Hertzman, Li,&Power, 2013). In summary, a stressful event causes a variety of physiological reactions that activate the adrenal glands, which in turn release epinephrine, norepinephrine, and cortisol. These hormones affect a number of bodily processes in ways that prepare the stressed person to take direct action, but also in ways that may heighten the potential for illness.
When stress is extreme or chronic, it can have profoundly negative consequences. For example, stress often contributes to the development of certain psychological disorders, including post-traumatic stress disorder, major depressive disorder, and other serious psychiatric conditions. Additionally, we noted earlier that stress is linked to the development and progression of a variety of physical illnesses and diseases. For example, researchers in one study found that people injured during the September 11, 2001, World Trade Center disaster or who developed post-traumatic stress symptoms afterward later suffered significantly elevated rates of heart disease (Jordan, Miller-Archie, Cone, Morabia,&Stellman, 2011). Another investigation yielded that self-reported stress symptoms among aging and retired Finnish food industry workers were associated with morbidity 11 years later. This study also predicted the onset of musculoskeletal, nervous system, and endocrine and metabolic disorders (Salonen, Arola, Nygård,&Huhtala, 2008). Another study reported that male South Korean manufacturing employees who reported high levels of work-related stress were more likely to catch the common cold over the next several months than were those employees who reported lower work-related stress levels (Park et al., 2011). Later, you will explore the mechanisms through which stress can produce physical illness and disease.
Stress is a process whereby an individual perceives and responds to events appraised as overwhelming or threatening to one’s well-being. The scientific study of how stress and emotional factors impact health and well-being is called health psychology, a field devoted to studying the general impact of psychological factors on health. The body’s primary physiological response during stress, the fight-or-flight response, was first identified in the early 20th century by Walter Cannon. The fight-or-flight response involves the coordinated activity of both the sympathetic nervous system and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. Hans Selye, a noted endocrinologist, referred to these physiological reactions to stress as part of general adaptation syndrome, which occurs in three stages: alarm reaction (fight-or-flight reactions begin), resistance (the body begins to adapt to continuing stress), and exhaustion (adaptive energy is depleted, and stress begins to take a physical toll).
Think of a time in which you and others you know (family members, friends, and classmates) experienced an event that some viewed as threatening and others viewed as challenging. What were some of the differences in the reactions of those who experienced the event as threatening compared to those who viewed the event as challenging? Why do you think there were differences in how these individuals judged the same event?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?