| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Visual and auditory stimuli both occur in the form of waves. Although the two stimuli are very different in terms of composition, wave forms share similar characteristics that are especially important to our visual and auditory perceptions. In this section, we describe the physical properties of the waves as well as the perceptual experiences associated with them.
Two physical characteristics of a wave are amplitude and wavelength ( [link] ). The amplitude of a wave is the height of a wave as measured from the highest point on the wave ( peak or crest ) to the lowest point on the wave ( trough ). Wavelength refers to the length of a wave from one peak to the next.
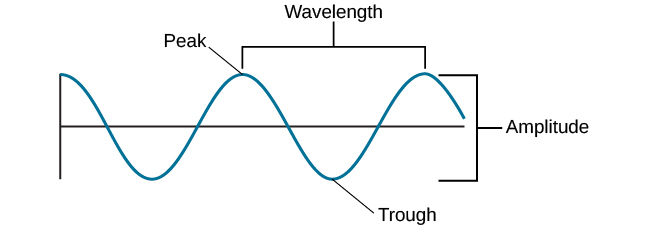
Wavelength is directly related to the frequency of a given wave form. Frequency refers to the number of waves that pass a given point in a given time period and is often expressed in terms of hertz (Hz) , or cycles per second. Longer wavelengths will have lower frequencies, and shorter wavelengths will have higher frequencies ( [link] ).

The visible spectrum is the portion of the larger electromagnetic spectrum that we can see. As [link] shows, the electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all of the electromagnetic radiation that occurs in our environment and includes gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet light, visible light, infrared light, microwaves, and radio waves. The visible spectrum in humans is associated with wavelengths that range from 380 to 740 nm—a very small distance, since a nanometer (nm) is one billionth of a meter. Other species can detect other portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. For instance, honeybees can see light in the ultraviolet range (Wakakuwa, Stavenga,&Arikawa, 2007), and some snakes can detect infrared radiation in addition to more traditional visual light cues (Chen, Deng, Brauth, Ding,&Tang, 2012; Hartline, Kass,&Loop, 1978).
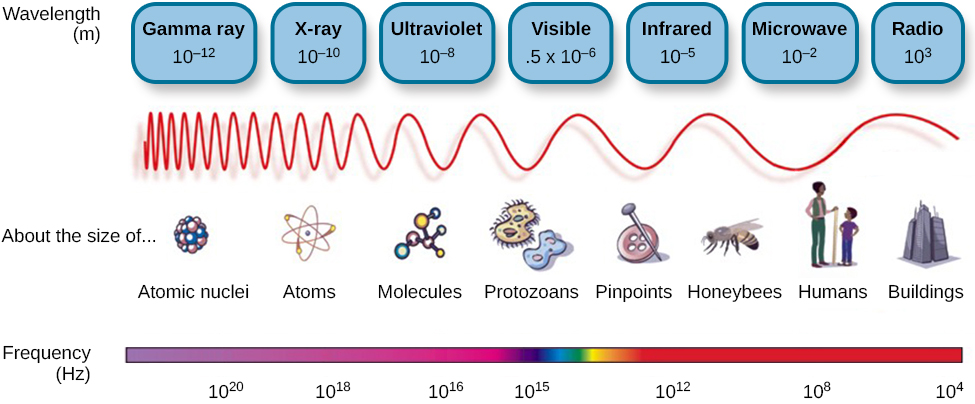
In humans, light wavelength is associated with perception of color ( [link] ). Within the visible spectrum, our experience of red is associated with longer wavelengths, greens are intermediate, and blues and violets are shorter in wavelength. (An easy way to remember this is the mnemonic ROYGBIV: r ed, o range, y ellow, g reen, b lue, i ndigo, v iolet.) The amplitude of light waves is associated with our experience of brightness or intensity of color, with larger amplitudes appearing brighter.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?