| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Electrons can be considered as a stream of waves that hit a surface and are diffracted by regions with high electron density (the atoms). The electrons in the range of 20 to 200 eV can penetrate the sample for about 10 Å without loosing energy. Because of this reason, LEED is especially sensitive to surfaces, unlike X-ray diffraction, which gives information about the bulk-structure of a crystal due to its larger mean free path (around micrometers). [link] compares general aspects of both techniques.
| Low energy electron diffraction | X-ray diffraction |
| Surface structure determination (high surface sensitivity) | Bulk structures determination |
| Sample single crystal | Sample single-crystal or polycrystalline |
| Sample must be have an oriented surface, sensitive to impurities | Surface impurities not important |
| Experiment in ultra-high vacuum | Experiment usually at atmospheric pressure |
| Experiment done mostly at constant incidence angle and variable wavelength (electron energy) | Constant wavelength and variable incidence angle |
| Diffraction pattern consists of beams visible at almost all energies | Diffraction pattern consists of beams flashing out at specific wavelengths and angles |
Like X-ray diffraction, electron diffraction also follows the Bragg’s law, see [link] , where λ is the wavelength, a is the atomic spacing, d is the spacing of the crystal layers, θ is the angle between the incident beam and the reflected beam, and n is an integer. For constructive interference between two waves, the path length difference (2a sinθ / 2d sinθ) must be an integral multiple of the wavelength.

In LEED, the diffracted beams impact on a fluorescent screen and form a pattern of light spots ( [link] a), which is a to-scale version of the reciprocal lattice of the unit cell. The reciprocal lattice is a set of imaginary points, where the direction of a vector from one point to another point is equal to the direction of a normal to one plane of atoms in the unit cell (real space). For example, an electron beam penetrates a few 2D-atomic layers, [link] b, so the reciprocal lattice seen by LEED consists of continues rods and discrete points per atomic layer, see [link] c. In this way, LEED patterns can give information about the size and shape of the real space unit cell, but nothing about the positions of the atoms. To gain this information about atomic positions, analysis of the spot intensities is required. For further information about reciprocal lattice and crystals refer to Crystal Structure and An Introduction to Single-Crystal X-Ray Crystallography .
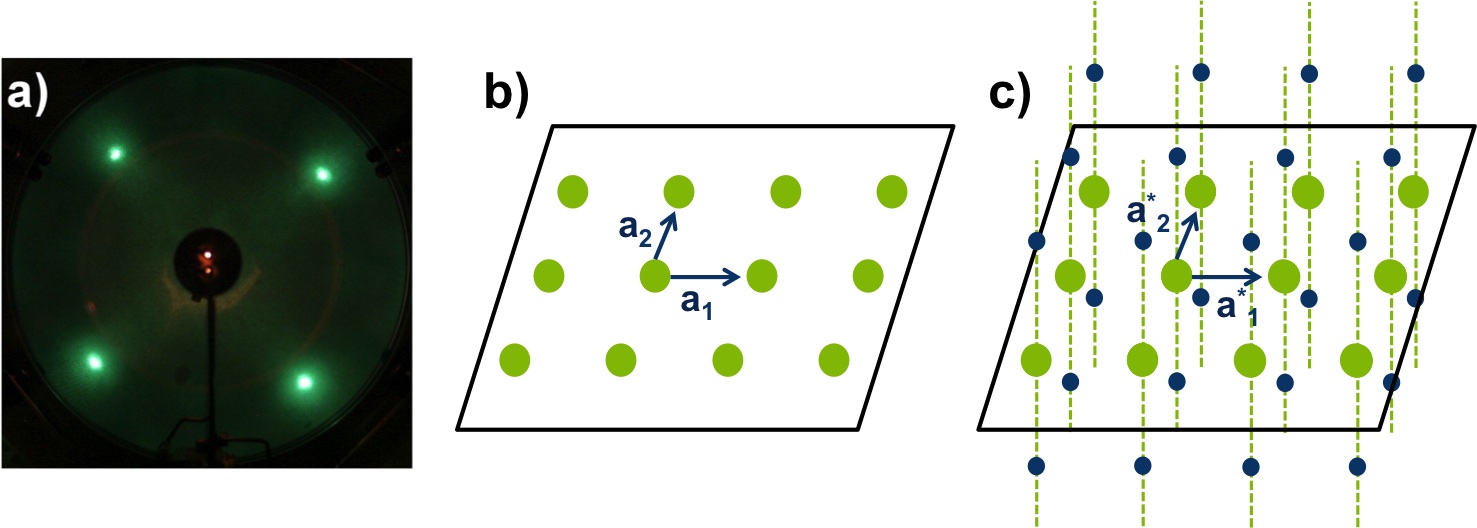
Thanks to the hemispheric geometry of the green screen of LEED, we can observe the reciprocal lattice without distortion. It is important to take into account that the separation of the points in the reciprocal lattice and the real interplanar distance are inversely proportional, which means that if the atoms are more widely spaced, the spots in the pattern get closer and vice versa. In the case of superlattices, a periodic structure composed of layers of two materials, new points arise in addition to the original diffraction pattern.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?