| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Analyzing the interference of light passing through two slits lays out the theoretical framework of interference and gives us a historical insight into Thomas Young’s experiments. However, much of the modern-day application of slit interference uses not just two slits but many, approaching infinity for practical purposes. The key optical element is called a diffraction grating, an important tool in optical analysis, which we discuss in detail in Diffraction . Here, we start the analysis of multiple-slit interference by taking the results from our analysis of the double slit ( ) and extending it to configurations with three, four, and much larger numbers of slits.
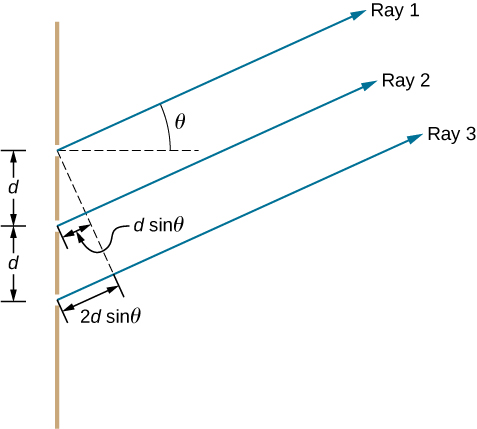
[link] shows the simplest case of multiple-slit interference, with three slits, or . The spacing between slits is d , and the path length difference between adjacent slits is , same as the case for the double slit. What is new is that the path length difference for the first and the third slits is . The condition for constructive interference is the same as for the double slit, that is
When this condition is met, is automatically a multiple of , so all three rays combine constructively, and the bright fringes that occur here are called principal maxima . But what happens when the path length difference between adjacent slits is only ? We can think of the first and second rays as interfering destructively, but the third ray remains unaltered. Instead of obtaining a dark fringe, or a minimum, as we did for the double slit, we see a secondary maximum with intensity lower than the principal maxima.
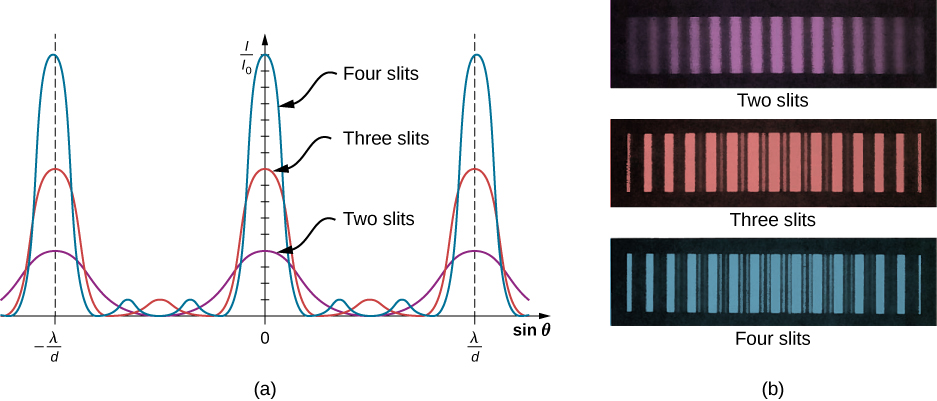
In general, for N slits, these secondary maxima occur whenever an unpaired ray is present that does not go away due to destructive interference. This occurs at evenly spaced positions between the principal maxima. The amplitude of the electromagnetic wave is correspondingly diminished to of the wave at the principal maxima, and the light intensity, being proportional to the square of the wave amplitude, is diminished to of the intensity compared to the principal maxima. As [link] shows, a dark fringe is located between every maximum (principal or secondary). As N grows larger and the number of bright and dark fringes increase, the widths of the maxima become narrower due to the closely located neighboring dark fringes. Because the total amount of light energy remains unaltered, narrower maxima require that each maximum reaches a correspondingly higher intensity.
Ten narrow slits are equally spaced 0.25 mm apart and illuminated with yellow light of wavelength 580 nm. (a) What are the angular positions of the third and fourth principal maxima? (b) What is the separation of these maxima on a screen 2.0 m from the slits?
a. b.
The width of bright fringes can be calculated as the separation between the two adjacent dark fringes on either side. Find the angular widths of the third- and fourth-order bright fringes from the preceding problem.
For a three-slit interference pattern, find the ratio of the peak intensities of a secondary maximum to a principal maximum.
1:9
What is the angular width of the central fringe of the interference pattern of (a) 20 slits separated by ? (b) 50 slits with the same separation? Assume that .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?