| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
You only have to look as far as the nearest bathroom to find an example of an image formed by a mirror. Images in a plane mirror are the same size as the object, are located behind the mirror, and are oriented in the same direction as the object (i.e., “upright”).
To understand how this happens, consider [link] . Two rays emerge from point P , strike the mirror, and reflect into the observer’s eye. Note that we use the law of reflection to construct the reflected rays. If the reflected rays are extended backward behind the mirror (see dashed lines in [link] ), they seem to originate from point Q . This is where the image of point P is located. If we repeat this process for point , we obtain its image at point . You should convince yourself by using basic geometry that the image height (the distance from Q to ) is the same as the object height (the distance from P to ). By forming images of all points of the object, we obtain an upright image of the object behind the mirror.
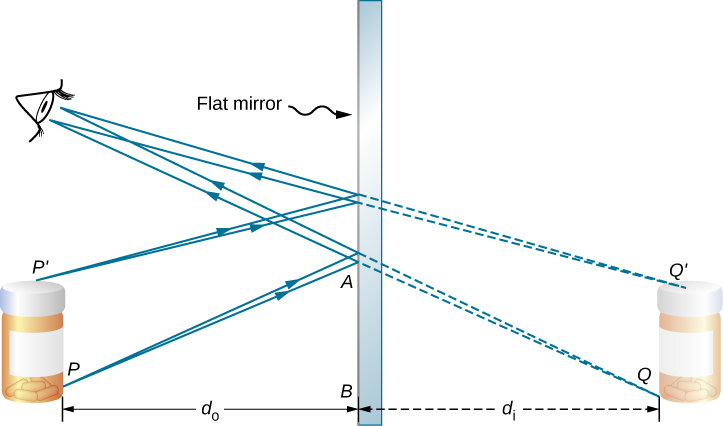
Notice that the reflected rays appear to the observer to come directly from the image behind the mirror. In reality, these rays come from the points on the mirror where they are reflected. The image behind the mirror is called a virtual image because it cannot be projected onto a screen—the rays only appear to originate from a common point behind the mirror. If you walk behind the mirror, you cannot see the image, because the rays do not go there. However, in front of the mirror, the rays behave exactly as if they come from behind the mirror, so that is where the virtual image is located.
Later in this chapter, we discuss real images; a real image can be projected onto a screen because the rays physically go through the image. You can certainly see both real and virtual images. The difference is that a virtual image cannot be projected onto a screen, whereas a real image can.
The law of reflection tells us that the angle of incidence is the same as the angle of reflection. Applying this to triangles PAB and QAB in [link] and using basic geometry shows that they are congruent triangles. This means that the distance PB from the object to the mirror is the same as the distance BQ from the mirror to the image. The object distance (denoted ) is the distance from the mirror to the object (or, more generally, from the center of the optical element that creates its image). Similarly, the image distance (denoted ) is the distance from the mirror to the image (or, more generally, from the center of the optical element that creates it). If we measure distances from the mirror, then the object and image are in opposite directions, so for a plane mirror, the object and image distances should have the opposite signs:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?