| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
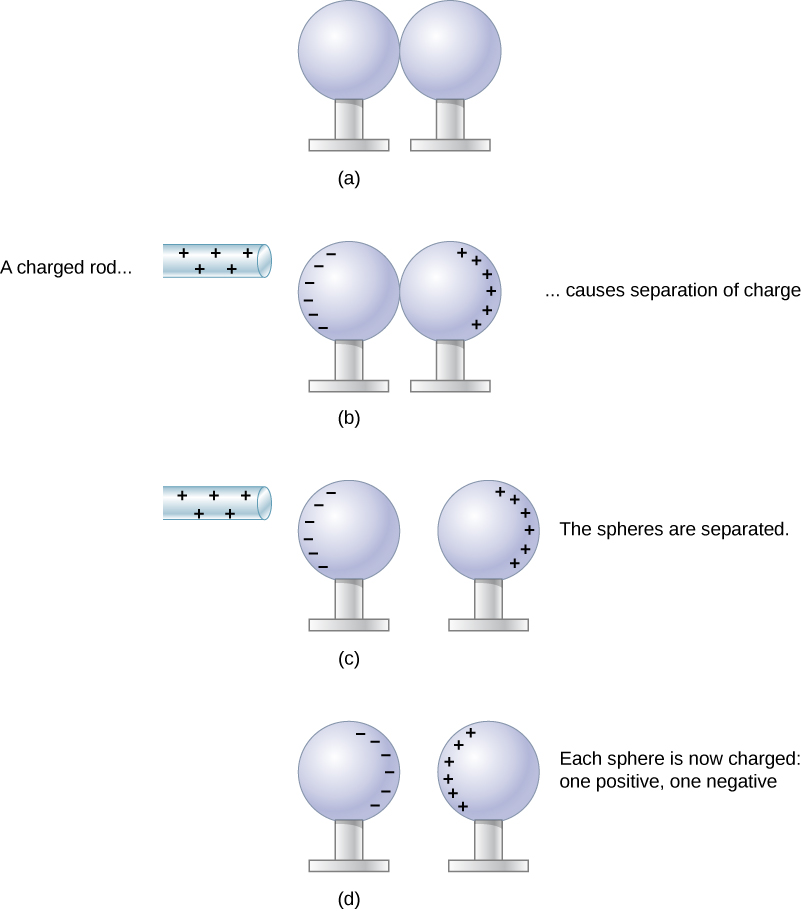
When the two ends of a dipole can be separated, this method of charging by induction may be used to create charged objects without transferring charge. In [link] , we see two neutral metal spheres in contact with one another but insulated from the rest of the world. A positively charged rod is brought near one of them, attracting negative charge to that side, leaving the other sphere positively charged.
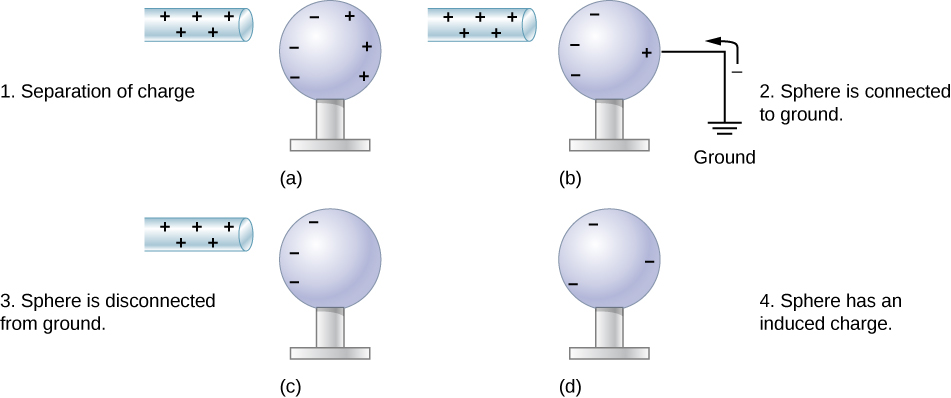
Another method of charging by induction is shown in [link] . The neutral metal sphere is polarized when a charged rod is brought near it. The sphere is then grounded, meaning that a conducting wire is run from the sphere to the ground. Since Earth is large and most of the ground is a good conductor, it can supply or accept excess charge easily. In this case, electrons are attracted to the sphere through a wire called the ground wire, because it supplies a conducting path to the ground. The ground connection is broken before the charged rod is removed, leaving the sphere with an excess charge opposite to that of the rod. Again, an opposite charge is achieved when charging by induction, and the charged rod loses none of its excess charge.
An eccentric inventor attempts to levitate a cork ball by wrapping it with foil and placing a large negative charge on the ball and then putting a large positive charge on the ceiling of his workshop. Instead, while attempting to place a large negative charge on the ball, the foil flies off. Explain.
When a glass rod is rubbed with silk, it becomes positive and the silk becomes negative—yet both attract dust. Does the dust have a third type of charge that is attracted to both positive and negative? Explain.
No, the dust is attracted to both because the dust particle molecules become polarized in the direction of the silk.
Why does a car always attract dust right after it is polished? (Note that car wax and car tires are insulators.)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?