| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The effects of an undesirable electric shock can vary in severity: a slight sensation at the point of contact, pain, loss of voluntary muscle control, difficulty breathing, heart fibrillation, and possibly death. The loss of voluntary muscle control can cause the victim to not be able to let go of the source of the current.
The major factors upon which the severity of the effects of electrical shock depend are
Our bodies are relatively good electric conductors due to the body’s water content. A dangerous condition occurs when the body is in contact with a voltage source and “ground.” The term “ground” refers to a large sink or source of electrons, for example, the earth (thus, the name). When there is a direct path to ground, large currents will pass through the parts of the body with the lowest resistance and a direct path to ground. A safety precaution used by many professions is the wearing of insulated shoes. Insulated shoes prohibit a pathway to ground for electrons through the feet by providing a large resistance. Whenever working with high-power tools, or any electric circuit, ensure that you do not provide a pathway for current flow (especially across the heart). A common safety precaution is to work with one hand, reducing the possibility of providing a current path through the heart.
Very small currents pass harmlessly and unfelt through the body. This happens to you regularly without your knowledge. The threshold of sensation is only 1 mA and, although unpleasant, shocks are apparently harmless for currents less than 5 mA. A great number of safety rules take the 5-mA value for the maximum allowed shock. At 5–30 mA and above, the current can stimulate sustained muscular contractions, much as regular nerve impulses do ( [link] ). Very large currents (above 300 mA) cause the heart and diaphragm of the lung to contract for the duration of the shock. Both the heart and respiration stop. Both often return to normal following the shock.
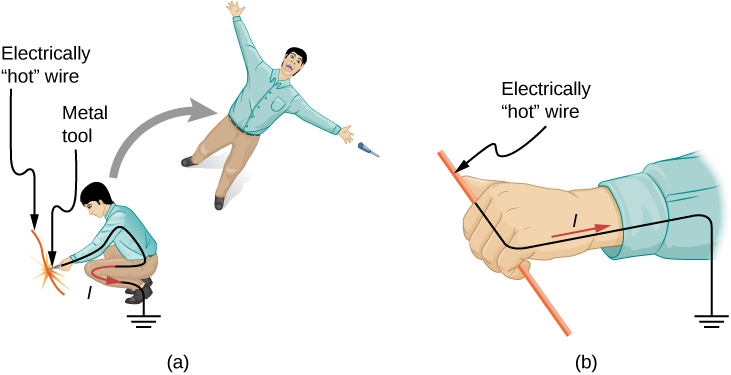
Current is the major factor determining shock severity. A larger voltage is more hazardous, but since the severity of the shock depends on the combination of voltage and resistance. For example, a person with dry skin has a resistance of about . If he comes into contact with 120-V ac, a current
passes harmlessly through him. The same person soaking wet may have a resistance of and the same 120 V will produce a current of 12 mA—above the “can’t let go” threshold and potentially dangerous.
[link] (a) shows the schematic for a simple ac circuit with no safety features. This is not how power is distributed in practice. Modern household and industrial wiring requires the three-wire system , shown schematically in part (b), which has several safety features, with live, neutral, and ground wires. First is the familiar circuit breaker (or fuse) to prevent thermal overload. Second is a protective case around the appliance, such as a toaster or refrigerator. The case’s safety feature is that it prevents a person from touching exposed wires and coming into electrical contact with the circuit, helping prevent shocks.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?