| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We discussed the concepts of work and energy earlier in mechanics. Examples and related issues of heat transfer between different objects have also been discussed in the preceding chapters. Here, we want to expand these concepts to a thermodynamic system and its environment. Specifically, we elaborated on the concepts of heat and heat transfer in the previous two chapters. Here, we want to understand how work is done by or to a thermodynamic system; how heat is transferred between a system and its environment; and how the total energy of the system changes under the influence of the work done and heat transfer.
A force created from any source can do work by moving an object through a displacement. Then how does a thermodynamic system do work? [link] shows a gas confined to a cylinder that has a movable piston at one end. If the gas expands against the piston, it exerts a force through a distance and does work on the piston. If the piston compresses the gas as it is moved inward, work is also done—in this case, on the gas. The work associated with such volume changes can be determined as follows: Let the gas pressure on the piston face be p . Then the force on the piston due to the gas is pA , where A is the area of the face. When the piston is pushed outward an infinitesimal distance dx , the magnitude of the work done by the gas is
Since the change in volume of the gas is this becomes
For a finite change in volume from we can integrate this equation from to find the net work:
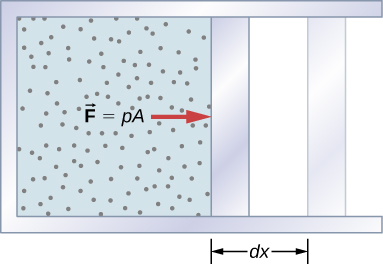
This integral is only meaningful for a quasi-static process , which means a process that takes place in infinitesimally small steps, keeping the system at thermal equilibrium. (We examine this idea in more detail later in this chapter.) Only then does a well-defined mathematical relationship (the equation of state) exist between the pressure and volume. This relationship can be plotted on a pV diagram of pressure versus volume, where the curve is the change of state. We can approximate such a process as one that occurs slowly, through a series of equilibrium states. The integral is interpreted graphically as the area under the pV curve (the shaded area of [link] ). Work done by the gas is positive for expansion and negative for compression.

Consider the two processes involving an ideal gas that are represented by paths AC and ABC in [link] . The first process is an isothermal expansion , with the volume of the gas changing its volume from . This isothermal process is represented by the curve between points A and C . The gas is kept at a constant temperature T by keeping it in thermal equilibrium with a heat reservoir at that temperature. From [link] and the ideal gas law,

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?