| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A thermodynamic system includes anything whose thermodynamic properties are of interest. It is embedded in its surroundings or environment ; it can exchange heat with, and do work on, its environment through a boundary , which is the imagined wall that separates the system and the environment ( [link] ). In reality, the immediate surroundings of the system are interacting with it directly and therefore have a much stronger influence on its behavior and properties. For example, if we are studying a car engine, the burning gasoline inside the cylinder of the engine is the thermodynamic system; the piston, exhaust system, radiator, and air outside form the surroundings of the system. The boundary then consists of the inner surfaces of the cylinder and piston.
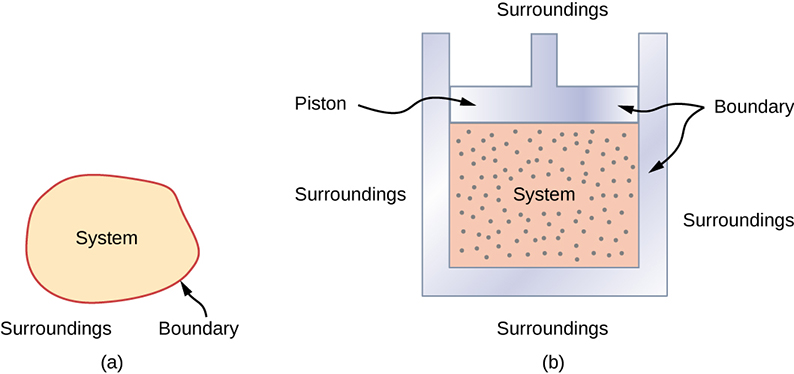
Normally, a system must have some interactions with its surroundings. A system is called an isolated or closed system if it is completely separated from its environment—for example, a gas that is surrounded by immovable and thermally insulating walls. In reality, a closed system does not exist unless the entire universe is treated as the system, or it is used as a model for an actual system that has minimal interactions with its environment. Most systems are known as an open system , which can exchange energy and/or matter with its surroundings ( [link] ).
When we examine a thermodynamic system, we ignore the difference in behavior from place to place inside the system for a given moment. In other words, we concentrate on the macroscopic properties of the system, which are the averages of the microscopic properties of all the molecules or entities in the system. Any thermodynamic system is therefore treated as a continuum that has the same behavior everywhere inside. We assume the system is in equilibrium . You could have, for example, a temperature gradient across the system. However, when we discuss a thermodynamic system in this chapter, we study those that have uniform properties throughout the system.
Before we can carry out any study on a thermodynamic system, we need a fundamental characterization of the system. When we studied a mechanical system, we focused on the forces and torques on the system, and their balances dictated the mechanical equilibrium of the system. In a similar way, we should examine the heat transfer between a thermodynamic system and its environment or between the different parts of the system, and its balance should dictate the thermal equilibrium of the system. Intuitively, such a balance is reached if the temperature becomes the same for different objects or parts of the system in thermal contact, and the net heat transfer over time becomes zero.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?