| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this section, we study simple models of ac voltage sources connected to three circuit components: (1) a resistor, (2) a capacitor, and (3) an inductor. The power furnished by an ac voltage source has an emf given by
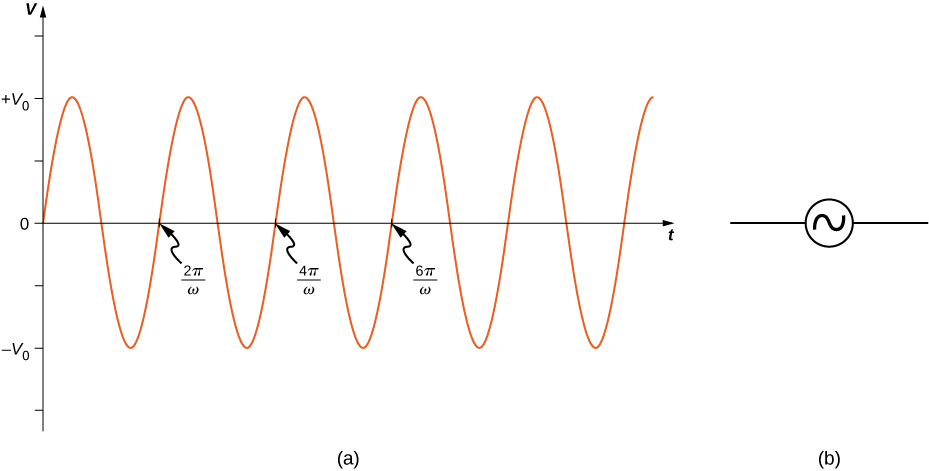
as shown in [link] . This sine function assumes we start recording the voltage when it is at a time of A phase constant may be involved that shifts the function when we start measuring voltages, similar to the phase constant in the waves we studied in Waves . However, because we are free to choose when we start examining the voltage, we can ignore this phase constant for now. We can measure this voltage across the circuit components using one of two methods: (1) a quantitative approach based on our knowledge of circuits, or (2) a graphical approach that is explained in the coming sections.
First, consider a resistor connected across an ac voltage source. From Kirchhoff’s loop rule, the instantaneous voltage across the resistor of [link] (a) is
and the instantaneous current through the resistor is
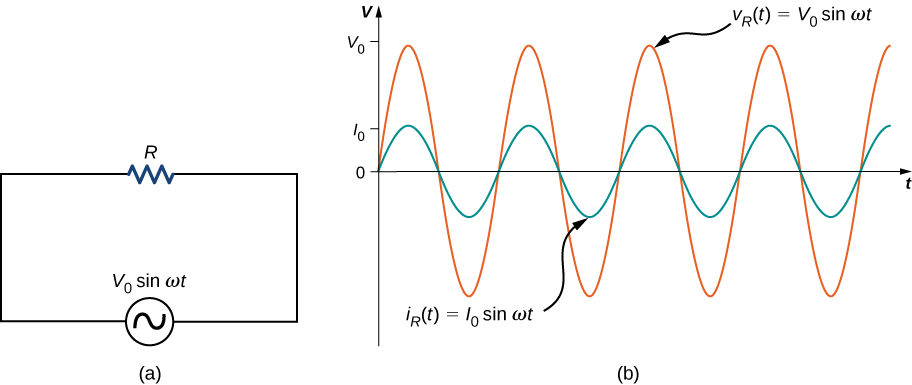
Here, is the amplitude of the time-varying current. Plots of and are shown in [link] (b). Both curves reach their maxima and minima at the same times, that is, the current through and the voltage across the resistor are in phase.
Graphical representations of the phase relationships between current and voltage are often useful in the analysis of ac circuits. Such representations are called phasor diagrams . The phasor diagram for is shown in [link] (a), with the current on the vertical axis. The arrow (or phasor) is rotating counterclockwise at a constant angular frequency so we are viewing it at one instant in time. If the length of the arrow corresponds to the current amplitude the projection of the rotating arrow onto the vertical axis is which is the instantaneous current.
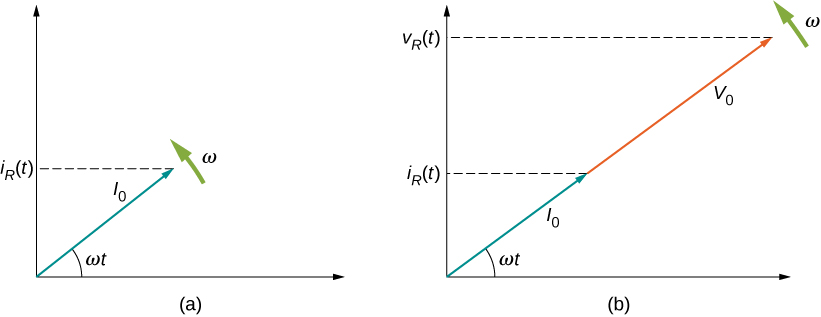
The vertical axis on a phasor diagram could be either the voltage or the current, depending on the phasor that is being examined. In addition, several quantities can be depicted on the same phasor diagram. For example, both the current and the voltage are shown in the diagram of [link] (b). Since they have the same frequency and are in phase, their phasors point in the same direction and rotate together. The relative lengths of the two phasors are arbitrary because they represent different quantities; however, the ratio of the lengths of the two phasors can be represented by the resistance, since one is a voltage phasor and the other is a current phasor.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?