| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
An example illustrating the independence of vertical and horizontal motions is given by two baseballs. One baseball is dropped from rest. At the same instant, another is thrown horizontally from the same height and it follows a curved path. A stroboscope captures the positions of the balls at fixed time intervals as they fall ( [link] ).
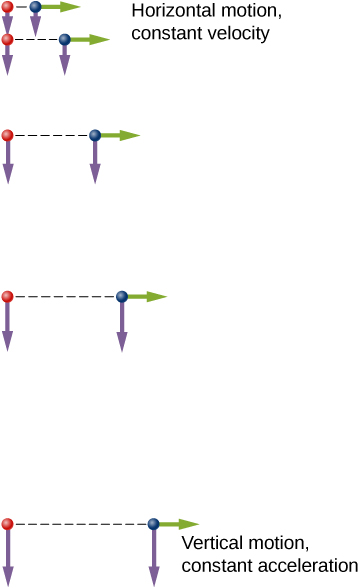
It is remarkable that for each flash of the strobe, the vertical positions of the two balls are the same. This similarity implies vertical motion is independent of whether the ball is moving horizontally. (Assuming no air resistance, the vertical motion of a falling object is influenced by gravity only, not by any horizontal forces.) Careful examination of the ball thrown horizontally shows it travels the same horizontal distance between flashes. This is because there are no additional forces on the ball in the horizontal direction after it is thrown. This result means horizontal velocity is constant and is affected neither by vertical motion nor by gravity (which is vertical). Note this case is true for ideal conditions only. In the real world, air resistance affects the speed of the balls in both directions.
The two-dimensional curved path of the horizontally thrown ball is composed of two independent one-dimensional motions (horizontal and vertical). The key to analyzing such motion, called projectile motion , is to resolve it into motions along perpendicular directions. Resolving two-dimensional motion into perpendicular components is possible because the components are independent.
What form does the trajectory of a particle have if the distance from any point A to point B is equal to the magnitude of the displacement from A to B ?
straight line
Give an example of a trajectory in two or three dimensions caused by independent perpendicular motions.
If the instantaneous velocity is zero, what can be said about the slope of the position function?
The slope must be zero because the velocity vector is tangent to the graph of the position function.
The coordinates of a particle in a rectangular coordinate system are (1.0, –4.0, 6.0). What is the position vector of the particle?
The position of a particle changes from to What is the particle’s displacement?
The 18th hole at Pebble Beach Golf Course is a dogleg to the left of length 496.0 m. The fairway off the tee is taken to be the x direction. A golfer hits his tee shot a distance of 300.0 m, corresponding to a displacement and hits his second shot 189.0 m with a displacement What is the final displacement of the golf ball from the tee?
A bird flies straight northeast a distance of 95.0 km for 3.0 h. With the x -axis due east and the y -axis due north, what is the displacement in unit vector notation for the bird? What is the average velocity for the trip?
A cyclist rides 5.0 km due east, then 10.0 km west of north. From this point she rides 8.0 km due west. What is the final displacement from where the cyclist started?
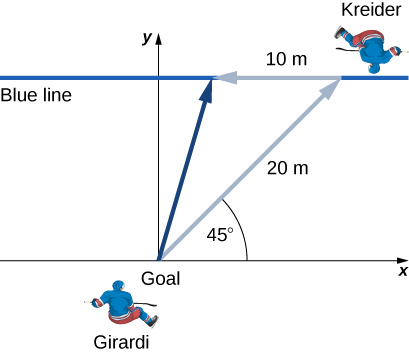
New York Rangers defenseman Daniel Girardi stands at the goal and passes a hockey puck 20 m and from straight down the ice to left wing Chris Kreider waiting at the blue line. Kreider waits for Girardi to reach the blue line and passes the puck directly across the ice to him 10 m away. What is the final displacement of the puck? See the following figure.
The position of a particle is (a) What is the velocity of the particle at 0 s and at s? (b) What is the average velocity between 0 s and s?
a.
,
b.
Clay Matthews, a linebacker for the Green Bay Packers, can reach a speed of 10.0 m/s. At the start of a play, Matthews runs downfield at with respect to the 50-yard line and covers 8.0 m in 1 s. He then runs straight down the field at with respect to the 50-yard line for 12 m, with an elapsed time of 1.2 s. (a) What is Matthews’ final displacement from the start of the play? (b) What is his average velocity?
The F-35B Lighting II is a short-takeoff and vertical landing fighter jet. If it does a vertical takeoff to 20.00-m height above the ground and then follows a flight path angled at with respect to the ground for 20.00 km, what is the final displacement?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?