| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Check Your Understanding (a) Draw the free-body diagram for the situation shown. (b) Redraw it showing components; use x -axes parallel to the two ramps.

_img.jpg) ;
;
_img.jpg)
View this simulation to predict, qualitatively, how an external force will affect the speed and direction of an object’s motion. Explain the effects with the help of a free-body diagram. Use free-body diagrams to draw position, velocity, acceleration, and force graphs, and vice versa. Explain how the graphs relate to one another. Given a scenario or a graph, sketch all four graphs.
| Net external force | |
| Newton’s first law | |
| Newton’s second law, vector form | |
| Newton’s second law, scalar form | |
| Newton’s second law, component form | |
| Newton’s second law, momentum form | |
| Definition of weight, vector form | |
| Definition of weight, scalar form | |
| Newton’s third law | |
| Normal force on an object resting on a
horizontal surface, vector form |
|
| Normal force on an object resting on a
horizontal surface, scalar form |
|
| Normal force on an object resting on an
inclined plane, scalar form |
|
| Tension in a cable supporting an object
of mass m at rest, scalar form |
In completing the solution for a problem involving forces, what do we do after constructing the free-body diagram? That is, what do we apply?
If a book is located on a table, how many forces should be shown in a free-body diagram of the book? Describe them.
two forces of different types: weight acting downward and normal force acting upward
If the book in the previous question is in free fall, how many forces should be shown in a free-body diagram of the book? Describe them.
A ball of mass m hangs at rest, suspended by a string. (a) Sketch all forces. (b) Draw the free-body diagram for the ball.
A car moves along a horizontal road. Draw a free-body diagram; be sure to include the friction of the road that opposes the forward motion of the car.

A runner pushes against the track, as shown. (a) Provide a free-body diagram showing all the forces on the runner. ( Hint: Place all forces at the center of his body, and include his weight.) (b) Give a revised diagram showing the xy -component form.

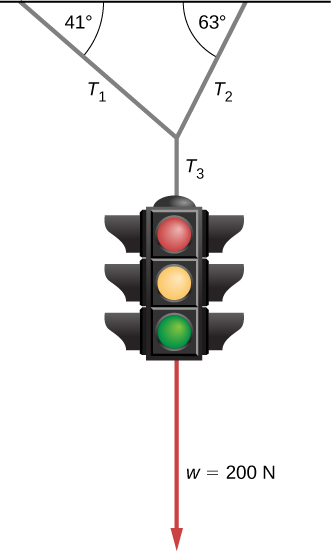
The traffic light hangs from the cables as shown. Draw a free-body diagram on a coordinate plane for this situation.

Two small forces, N and N, are exerted on a rogue asteroid by a pair of space tractors. (a) Find the net force. (b) What are the magnitude and direction of the net force? (c) If the mass of the asteroid is 125 kg, what acceleration does it experience (in vector form)? (d) What are the magnitude and direction of the acceleration?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?