| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Displacement and velocity in two or three dimensions are straightforward extensions of the one-dimensional definitions. However, now they are vector quantities, so calculations with them have to follow the rules of vector algebra, not scalar algebra.
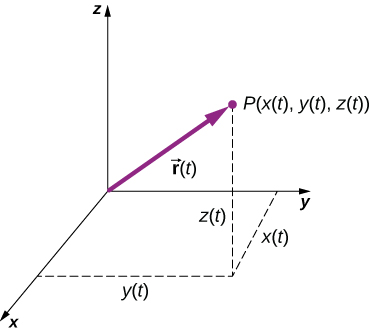
To describe motion in two and three dimensions, we must first establish a coordinate system and a convention for the axes. We generally use the coordinates x , y , and z to locate a particle at point P ( x , y , z ) in three dimensions. If the particle is moving, the variables x , y , and z are functions of time ( t ):
The position vector from the origin of the coordinate system to point P is In unit vector notation, introduced in Coordinate Systems and Components of a Vector , is
[link] shows the coordinate system and the vector to point P , where a particle could be located at a particular time t . Note the orientation of the x , y , and z axes. This orientation is called a right-handed coordinate system ( Coordinate Systems and Components of a Vector ) and it is used throughout the chapter.
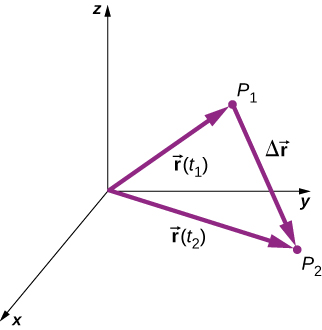
With our definition of the position of a particle in three-dimensional space, we can formulate the three-dimensional displacement. [link] shows a particle at time located at with position vector At a later time the particle is located at with position vector . The displacement vector is found by subtracting from
Vector addition is discussed in Vectors . Note that this is the same operation we did in one dimension, but now the vectors are in three-dimensional space.
The following examples illustrate the concept of displacement in multiple dimensions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?