| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We have just considered the energy of SHM as a function of time. Another interesting view of the simple harmonic oscillator is to consider the energy as a function of position. [link] shows a graph of the energy versus position of a system undergoing SHM.

The potential energy curve in [link] resembles a bowl. When a marble is placed in a bowl, it settles to the equilibrium position at the lowest point of the bowl . This happens because a restoring force points toward the equilibrium point. This equilibrium point is sometimes referred to as a fixed point . When the marble is disturbed to a different position , the marble oscillates around the equilibrium position. Looking back at the graph of potential energy, the force can be found by looking at the slope of the potential energy graph . Since the force on either side of the fixed point points back toward the equilibrium point, the equilibrium point is called a stable equilibrium point . The points and are called the turning points . (See Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy .)
Stability is an important concept. If an equilibrium point is stable, a slight disturbance of an object that is initially at the stable equilibrium point will cause the object to oscillate around that point. The stable equilibrium point occurs because the force on either side is directed toward it. For an unstable equilibrium point, if the object is disturbed slightly, it does not return to the equilibrium point.
Consider the marble in the bowl example. If the bowl is right-side up, the marble, if disturbed slightly, will oscillate around the stable equilibrium point. If the bowl is turned upside down, the marble can be balanced on the top, at the equilibrium point where the net force is zero. However, if the marble is disturbed slightly, it will not return to the equilibrium point, but will instead roll off the bowl. The reason is that the force on either side of the equilibrium point is directed away from that point. This point is an unstable equilibrium point.
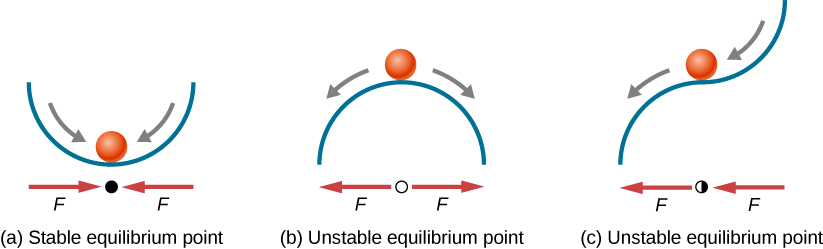
[link] shows three conditions. The first is a stable equilibrium point (a), the second is an unstable equilibrium point (b), and the last is also an unstable equilibrium point (c), because the force on only one side points toward the equilibrium point.
The process of determining whether an equilibrium point is stable or unstable can be formalized. Consider the potential energy curves shown in [link] . The force can be found by analyzing the slope of the graph. The force is In (a), the fixed point is at When the force is positive. When the force is negative. This is a stable point. In (b), the fixed point is at When the force is negative. When the force is also negative. This is an unstable point.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?