| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this section, we put together all the pieces learned so far in this chapter to analyze the dynamics of rotating rigid bodies. We have analyzed motion with kinematics and rotational kinetic energy but have not yet connected these ideas with force and/or torque. In this section, we introduce the rotational equivalent to Newton’s second law of motion and apply it to rigid bodies with fixed-axis rotation.
We have thus far found many counterparts to the translational terms used throughout this text, most recently, torque, the rotational analog to force. This raises the question: Is there an analogous equation to Newton’s second law, which involves torque and rotational motion? To investigate this, we start with Newton’s second law for a single particle rotating around an axis and executing circular motion. Let’s exert a force on a point mass m that is at a distance r from a pivot point ( [link] ). The particle is constrained to move in a circular path with fixed radius and the force is tangent to the circle. We apply Newton’s second law to determine the magnitude of the acceleration in the direction of . Recall that the magnitude of the tangential acceleration is proportional to the magnitude of the angular acceleration by . Substituting this expression into Newton’s second law, we obtain
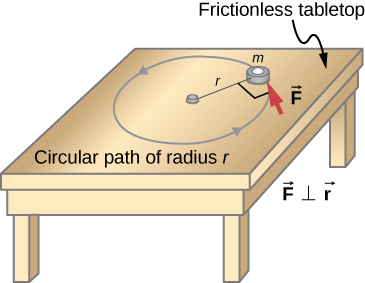
Multiply both sides of this equation by r ,
Note that the left side of this equation is the torque about the axis of rotation, where r is the lever arm and F is the force, perpendicular to r . Recall that the moment of inertia for a point particle is . The torque applied perpendicularly to the point mass in [link] is therefore
The torque on the particle is equal to the moment of inertia about the rotation axis times the angular acceleration . We can generalize this equation to a rigid body rotating about a fixed axis.
If more than one torque acts on a rigid body about a fixed axis, then the sum of the torques equals the moment of inertia times the angular acceleration:
The term is a scalar quantity and can be positive or negative (counterclockwise or clockwise) depending upon the sign of the net torque. Remember the convention that counterclockwise angular acceleration is positive. Thus, if a rigid body is rotating clockwise and experiences a positive torque (counterclockwise), the angular acceleration is positive.
[link] is Newton’s second law for rotation and tells us how to relate torque, moment of inertia, and rotational kinematics. This is called the equation for rotational dynamics . With this equation, we can solve a whole class of problems involving force and rotation. It makes sense that the relationship for how much force it takes to rotate a body would include the moment of inertia, since that is the quantity that tells us how easy or hard it is to change the rotational motion of an object.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?