| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When you pour yourself a glass of juice, the liquid flows freely and quickly. But when you pour syrup on your pancakes, that liquid flows slowly and sticks to the pitcher. The difference is fluid friction, both within the fluid itself and between the fluid and its surroundings. We call this property of fluids viscosity . Juice has low viscosity, whereas syrup has high viscosity. In the previous sections we have considered ideal fluids with little or no viscosity. In this section, we will investigate what factors, including viscosity, affect the rate of fluid flow.
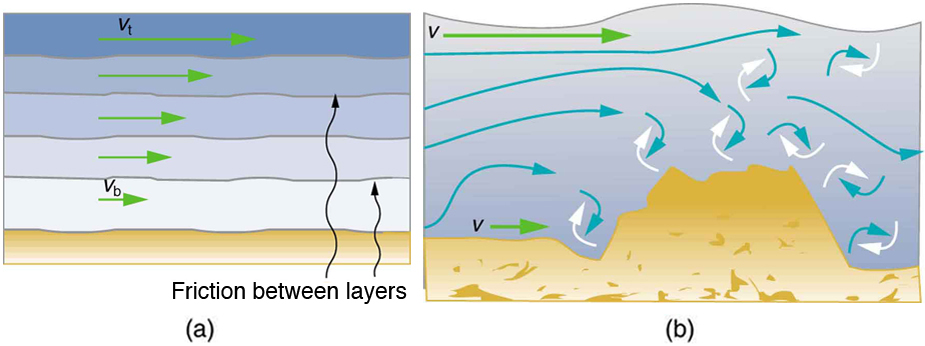
The precise definition of viscosity is based on laminar , or nonturbulent, flow. Before we can define viscosity, then, we need to define laminar flow and turbulent flow. [link] shows both types of flow. Laminar flow is characterized by the smooth flow of the fluid in layers that do not mix. Turbulent flow, or turbulence , is characterized by eddies and swirls that mix layers of fluid together.

[link] shows schematically how laminar and turbulent flow differ. Layers flow without mixing when flow is laminar. When there is turbulence, the layers mix, and there are significant velocities in directions other than the overall direction of flow. The lines that are shown in many illustrations are the paths followed by small volumes of fluids. These are called streamlines . Streamlines are smooth and continuous when flow is laminar, but break up and mix when flow is turbulent. Turbulence has two main causes. First, any obstruction or sharp corner, such as in a faucet, creates turbulence by imparting velocities perpendicular to the flow. Second, high speeds cause turbulence. The drag both between adjacent layers of fluid and between the fluid and its surroundings forms swirls and eddies, if the speed is great enough. We shall concentrate on laminar flow for the remainder of this section, leaving certain aspects of turbulence for later sections.
Try dropping simultaneously two sticks into a flowing river, one near the edge of the river and one near the middle. Which one travels faster? Why?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?