| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Children blow soap bubbles and play in the spray of a sprinkler on a hot summer day. (See [link] .) An underwater spider keeps his air supply in a shiny bubble he carries wrapped around him. A technician draws blood into a small-diameter tube just by touching it to a drop on a pricked finger. A premature infant struggles to inflate her lungs. What is the common thread? All these activities are dominated by the attractive forces between atoms and molecules in liquids—both within a liquid and between the liquid and its surroundings.
Attractive forces between molecules of the same type are called cohesive forces . Liquids can, for example, be held in open containers because cohesive forces hold the molecules together. Attractive forces between molecules of different types are called adhesive forces . Such forces cause liquid drops to cling to window panes, for example. In this section we examine effects directly attributable to cohesive and adhesive forces in liquids.
Attractive forces between molecules of the same type are called cohesive forces.
Attractive forces between molecules of different types are called adhesive forces.

Cohesive forces between molecules cause the surface of a liquid to contract to the smallest possible surface area. This general effect is called surface tension . Molecules on the surface are pulled inward by cohesive forces, reducing the surface area. Molecules inside the liquid experience zero net force, since they have neighbors on all sides.
Cohesive forces between molecules cause the surface of a liquid to contract to the smallest possible surface area. This general effect is called surface tension.
Forces between atoms and molecules underlie the macroscopic effect called surface tension. These attractive forces pull the molecules closer together and tend to minimize the surface area. This is another example of a submicroscopic explanation for a macroscopic phenomenon.
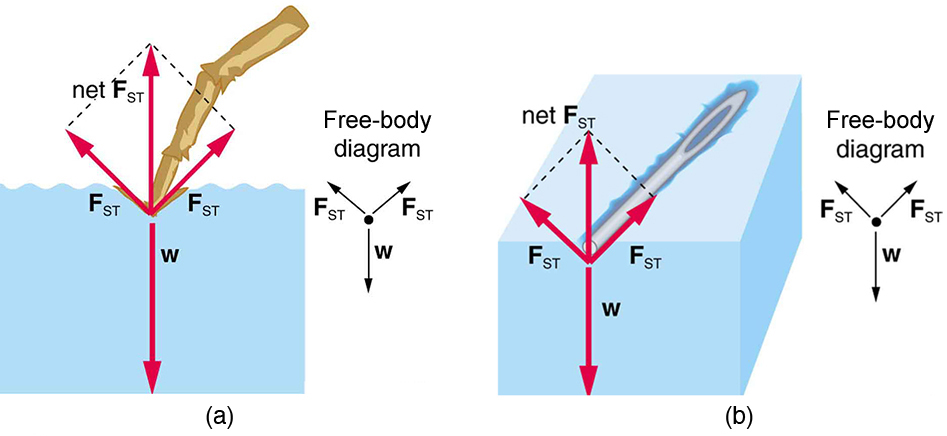
The model of a liquid surface acting like a stretched elastic sheet can effectively explain surface tension effects. For example, some insects can walk on water (as opposed to floating in it) as we would walk on a trampoline—they dent the surface as shown in [link] (a). [link] (b) shows another example, where a needle rests on a water surface. The iron needle cannot, and does not, float, because its density is greater than that of water. Rather, its weight is supported by forces in the stretched surface that try to make the surface smaller or flatter. If the needle were placed point down on the surface, its weight acting on a smaller area would break the surface, and it would sink.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?