| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

In this case, the total displacement is seen to have a magnitude of 50.0 m and to lie in a direction south of east. By using its magnitude and direction, this vector can be expressed as and south of east.
Discussion
The head-to-tail graphical method of vector addition works for any number of vectors. It is also important to note that the resultant is independent of the order in which the vectors are added. Therefore, we could add the vectors in any order as illustrated in [link] and we will still get the same solution.

Here, we see that when the same vectors are added in a different order, the result is the same. This characteristic is true in every case and is an important characteristic of vectors. Vector addition is commutative . Vectors can be added in any order.
(This is true for the addition of ordinary numbers as well—you get the same result whether you add or , for example).
Vector subtraction is a straightforward extension of vector addition. To define subtraction (say we want to subtract from , written , we must first define what we mean by subtraction. The negative of a vector is defined to be ; that is, graphically the negative of any vector has the same magnitude but the opposite direction , as shown in [link] . In other words, has the same length as , but points in the opposite direction. Essentially, we just flip the vector so it points in the opposite direction.
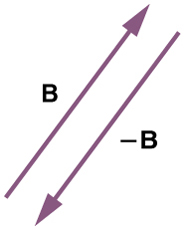
The subtraction of vector from vector is then simply defined to be the addition of to . Note that vector subtraction is the addition of a negative vector. The order of subtraction does not affect the results.
This is analogous to the subtraction of scalars (where, for example, ). Again, the result is independent of the order in which the subtraction is made. When vectors are subtracted graphically, the techniques outlined above are used, as the following example illustrates.
A woman sailing a boat at night is following directions to a dock. The instructions read to first sail 27.5 m in a direction north of east from her current location, and then travel 30.0 m in a direction north of east (or west of north). If the woman makes a mistake and travels in the opposite direction for the second leg of the trip, where will she end up? Compare this location with the location of the dock.

Strategy
We can represent the first leg of the trip with a vector , and the second leg of the trip with a vector . The dock is located at a location . If the woman mistakenly travels in the opposite direction for the second leg of the journey, she will travel a distance (30.0 m) in the direction south of east. We represent this as , as shown below. The vector has the same magnitude as but is in the opposite direction. Thus, she will end up at a location , or .
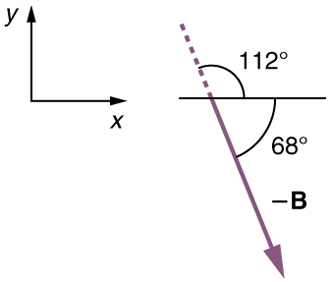
We will perform vector addition to compare the location of the dock, , with the location at which the woman mistakenly arrives, .
Solution
(1) To determine the location at which the woman arrives by accident, draw vectors and .
(2) Place the vectors head to tail.
(3) Draw the resultant vector .
(4) Use a ruler and protractor to measure the magnitude and direction of .

In this case, and south of east.
(5) To determine the location of the dock, we repeat this method to add vectors and . We obtain the resultant vector :
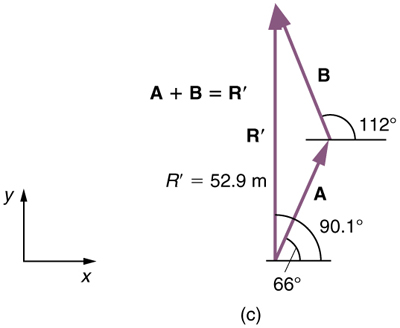
In this case and north of east.
We can see that the woman will end up a significant distance from the dock if she travels in the opposite direction for the second leg of the trip.
Discussion
Because subtraction of a vector is the same as addition of a vector with the opposite direction, the graphical method of subtracting vectors works the same as for addition.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?