| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The information presented in this section supports the following AP® learning objectives and science practices:
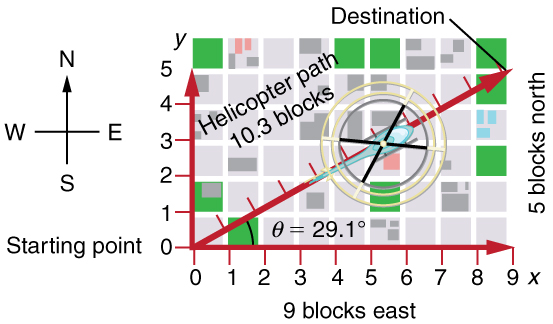
A vector is a quantity that has magnitude and direction. Displacement, velocity, acceleration, and force, for example, are all vectors. In one-dimensional, or straight-line, motion, the direction of a vector can be given simply by a plus or minus sign. In two dimensions (2-d), however, we specify the direction of a vector relative to some reference frame (i.e., coordinate system), using an arrow having length proportional to the vector's magnitude and pointing in the direction of the vector.
[link] shows such a graphical representation of a vector , using as an example the total displacement for the person walking in a city considered in Kinematics in Two Dimensions: An Introduction . We shall use the notation that a boldface symbol, such as , stands for a vector. Its magnitude is represented by the symbol in italics, , and its direction by .
In this text, we will represent a vector with a boldface variable. For example, we will represent the quantity force with the vector , which has both magnitude and direction. The magnitude of the vector will be represented by a variable in italics, such as , and the direction of the variable will be given by an angle .

The head-to-tail method is a graphical way to add vectors, described in [link] below and in the steps following. The tail of the vector is the starting point of the vector, and the head (or tip) of a vector is the final, pointed end of the arrow.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?