| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Now we substitute and from earlier equations into the above expression for energy. Algebraic manipulation yields
for the orbital energies of hydrogen-like atoms . Here, is the ground-state energy for hydrogen and is given by
Thus, for hydrogen,
[link] shows an energy-level diagram for hydrogen that also illustrates how the various spectral series for hydrogen are related to transitions between energy levels.
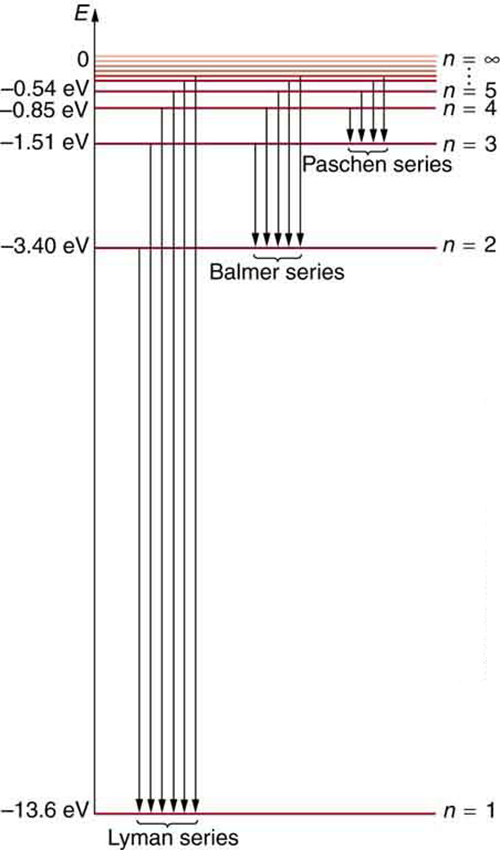
Electron total energies are negative, since the electron is bound to the nucleus, analogous to being in a hole without enough kinetic energy to escape. As approaches infinity, the total energy becomes zero. This corresponds to a free electron with no kinetic energy, since gets very large for large , and the electric potential energy thus becomes zero. Thus, 13.6 eV is needed to ionize hydrogen (to go from –13.6 eV to 0, or unbound), an experimentally verified number. Given more energy, the electron becomes unbound with some kinetic energy. For example, giving 15.0 eV to an electron in the ground state of hydrogen strips it from the atom and leaves it with 1.4 eV of kinetic energy.
Finally, let us consider the energy of a photon emitted in a downward transition, given by the equation to be
Substituting , we see that
Dividing both sides of this equation by gives an expression for :
It can be shown that
is the Rydberg constant . Thus, we have used Bohr’s assumptions to derive the formula first proposed by Balmer years earlier as a recipe to fit experimental data.
We see that Bohr’s theory of the hydrogen atom answers the question as to why this previously known formula describes the hydrogen spectrum. It is because the energy levels are proportional to , where is a non-negative integer. A downward transition releases energy, and so must be greater than . The various series are those where the transitions end on a certain level. For the Lyman series, — that is, all the transitions end in the ground state (see also [link] ). For the Balmer series, , or all the transitions end in the first excited state; and so on. What was once a recipe is now based in physics, and something new is emerging—angular momentum is quantized.
Bohr did what no one had been able to do before. Not only did he explain the spectrum of hydrogen, he correctly calculated the size of the atom from basic physics. Some of his ideas are broadly applicable. Electron orbital energies are quantized in all atoms and molecules. Angular momentum is quantized. The electrons do not spiral into the nucleus, as expected classically (accelerated charges radiate, so that the electron orbits classically would decay quickly, and the electrons would sit on the nucleus—matter would collapse). These are major triumphs.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?