| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Three rules that apply to electromagnetic waves in general are as follows:
Note that there are exceptions to these rules of thumb.
What happens when an electromagnetic wave impinges on a material? If the material is transparent to the particular frequency, then the wave can largely be transmitted. If the material is opaque to the frequency, then the wave can be totally reflected. The wave can also be absorbed by the material, indicating that there is some interaction between the wave and the material, such as the thermal agitation of molecules.
Of course it is possible to have partial transmission, reflection, and absorption. We normally associate these properties with visible light, but they do apply to all electromagnetic waves. What is not obvious is that something that is transparent to light may be opaque at other frequencies. For example, ordinary glass is transparent to visible light but largely opaque to ultraviolet radiation. Human skin is opaque to visible light—we cannot see through people—but transparent to X-rays.
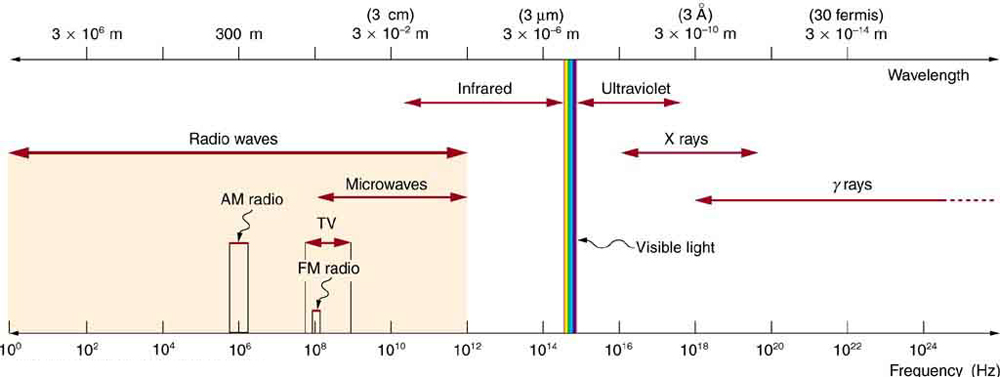
The broad category of radio waves is defined to contain any electromagnetic wave produced by currents in wires and circuits. Its name derives from their most common use as a carrier of audio information (i.e., radio). The name is applied to electromagnetic waves of similar frequencies regardless of source. Radio waves from outer space, for example, do not come from alien radio stations. They are created by many astronomical phenomena, and their study has revealed much about nature on the largest scales.
There are many uses for radio waves, and so the category is divided into many subcategories, including microwaves and those electromagnetic waves used for AM and FM radio, cellular telephones, and TV.
The lowest commonly encountered radio frequencies are produced by high-voltage AC power transmission lines at frequencies of 50 or 60 Hz. (See [link] .) These extremely long wavelength electromagnetic waves (about 6000 km!) are one means of energy loss in long-distance power transmission.
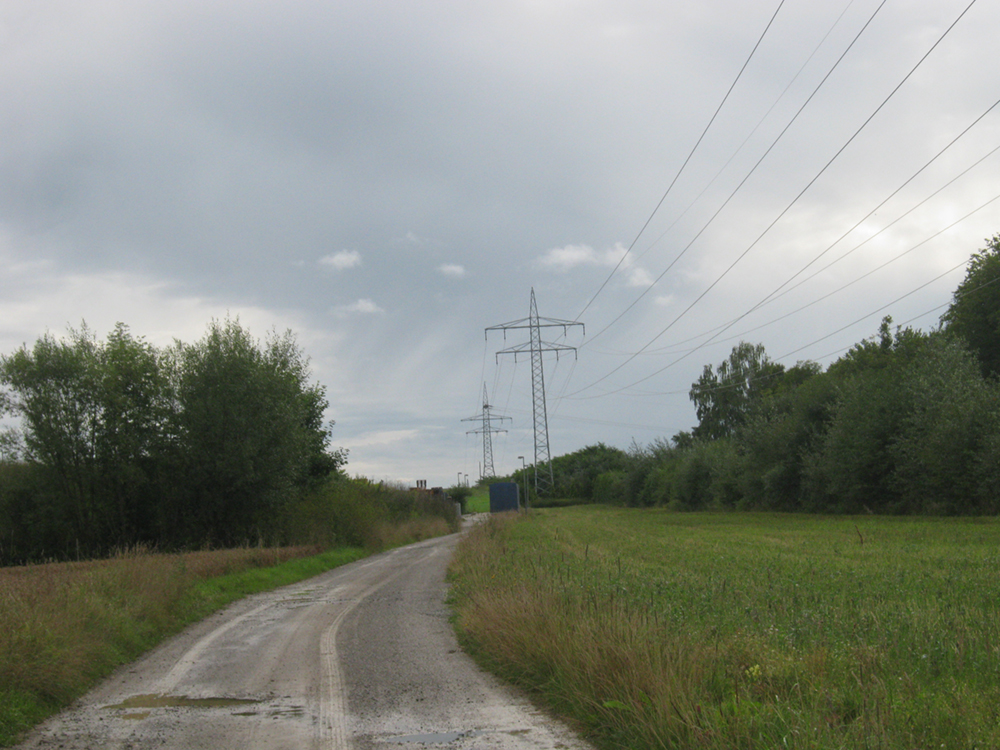

There is an ongoing controversy regarding potential health hazards associated with exposure to these electromagnetic fields ( -fields). Some people suspect that living near such transmission lines may cause a variety of illnesses, including cancer. But demographic data are either inconclusive or simply do not support the hazard theory. Recent reports that have looked at many European and American epidemiological studies have found no increase in risk for cancer due to exposure to -fields.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?