| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The information presented in this section supports the following AP® learning objectives and science practices:
How much current is needed to produce a significant magnetic field, perhaps as strong as the Earth’s field? Surveyors will tell you that overhead electric power lines create magnetic fields that interfere with their compass readings. Indeed, when Oersted discovered in 1820 that a current in a wire affected a compass needle, he was not dealing with extremely large currents. How does the shape of wires carrying current affect the shape of the magnetic field created? We noted earlier that a current loop created a magnetic field similar to that of a bar magnet, but what about a straight wire or a toroid (doughnut)? How is the direction of a current-created field related to the direction of the current? Answers to these questions are explored in this section, together with a brief discussion of the law governing the fields created by currents.
Magnetic fields have both direction and magnitude. As noted before, one way to explore the direction of a magnetic field is with compasses, as shown for a long straight current-carrying wire in [link] . Hall probes can determine the magnitude of the field. The field around a long straight wire is found to be in circular loops. The right hand rule 2 (RHR-2) emerges from this exploration and is valid for any current segment— point the thumb in the direction of the current, and the fingers curl in the direction of the magnetic field loops created by it.
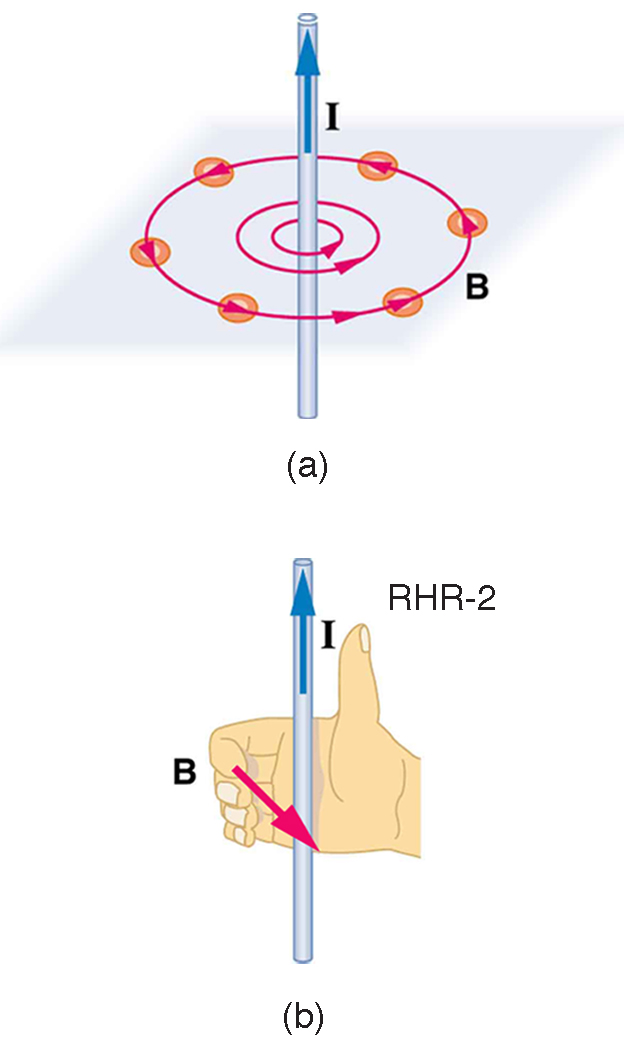
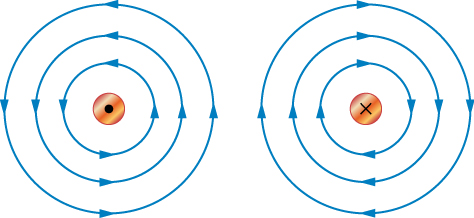
For a wire oriented perpendicular to the page, if the current in the wire is directed out of the page, the right-hand rule tells us that the magnetic field lines will be oriented in a counterclockwise direction around the wire. If the current in the wire is directed into the page, the magnetic field lines will be oriented in a clockwise direction around the wire. We use to indicate that the direction of the current in the wire is out of the page, and for the direction into the page.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?