| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The acceleration due to gravity on Earth differs slightly from place to place, depending on topography (e.g., whether you are on a hill or in a valley) and subsurface geology (whether there is dense rock like iron ore as opposed to light rock like salt beneath you.) The precise acceleration due to gravity can be calculated from data taken in an introductory physics laboratory course. An object, usually a metal ball for which air resistance is negligible, is dropped and the time it takes to fall a known distance is measured. See, for example, [link] . Very precise results can be produced with this method if sufficient care is taken in measuring the distance fallen and the elapsed time.
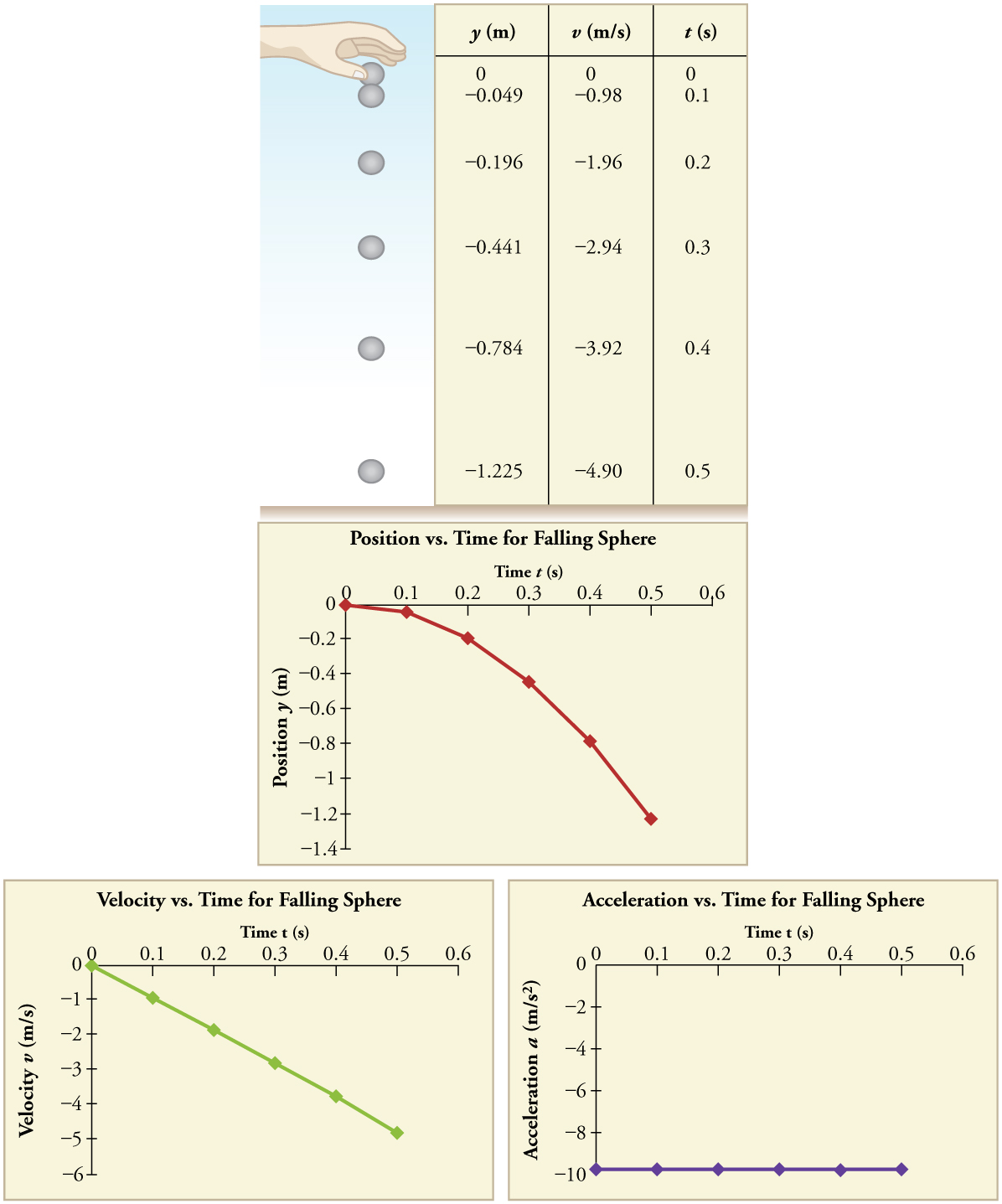
Suppose the ball falls 1.0000 m in 0.45173 s. Assuming the ball is not affected by air resistance, what is the precise acceleration due to gravity at this location?
Strategy
Draw a sketch.
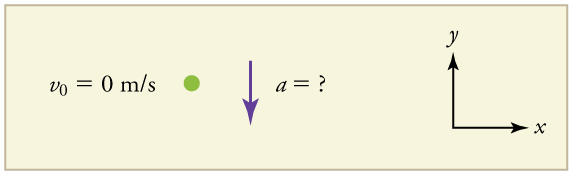
We need to solve for acceleration . Note that in this case, displacement is downward and therefore negative, as is acceleration.
Solution
1. Identify the knowns. ; ; ; .
2. Choose the equation that allows you to solve for using the known values.
3. Substitute 0 for and rearrange the equation to solve for . Substituting 0 for yields
Solving for gives
4. Substitute known values yields
so, because with the directions we have chosen,
Discussion
The negative value for indicates that the gravitational acceleration is downward, as expected. We expect the value to be somewhere around the average value of , so makes sense. Since the data going into the calculation are relatively precise, this value for is more precise than the average value of ; it represents the local value for the acceleration due to gravity.
While it is well established that the acceleration due to gravity is quite nearly 9.8 m/s 2 at all locations on Earth, you can verify this for yourself with some basic materials.
Your task is to find the acceleration due to gravity at your location. Achieving an acceleration of precisely 9.8 m/s 2 will be difficult. However, with good preparation and attention to detail, you should be able to get close. Before you begin working, consider the following questions.
What measurements will you need to take in order to find the acceleration due to gravity?
What relationships and equations found in this chapter may be useful in calculating the acceleration?
What variables will you need to hold constant?
What materials will you use to record your measurements?
Upon completing these four questions, record your procedure. Once recorded, you may carry out the experiment. If you find that your experiment cannot be carried out, you may revise your procedure.
Once you have found your experimental acceleration, compare it to the assumed value of 9.8 m/s 2 . If error exists, what were the likely sources of this error? How could you change your procedure in order to improve the accuracy of your findings?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?