| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Find the mass of the picture hanging from a steel nail as shown in [link] , given that the nail bends only . (Assume the shear modulus is known to two significant figures.)
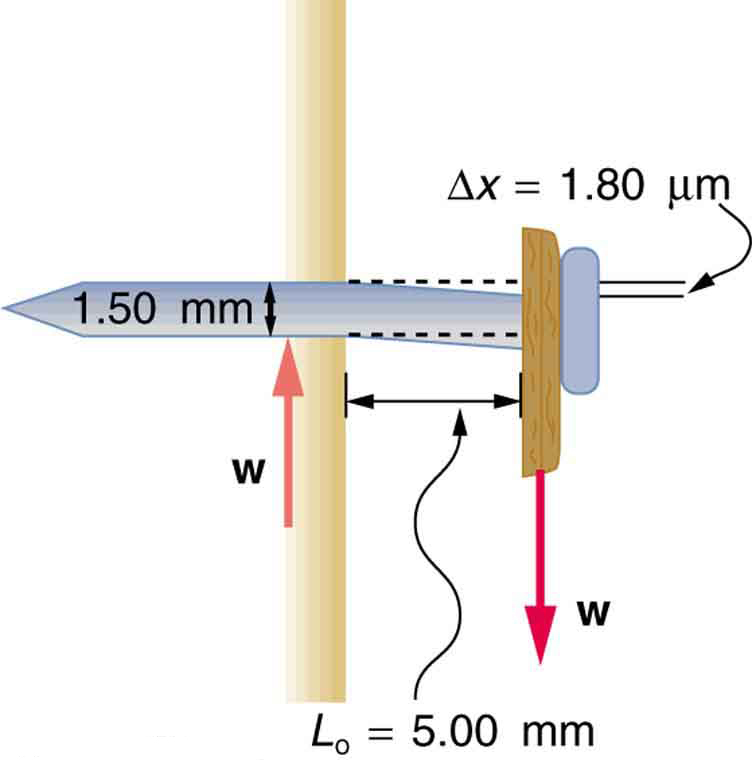
Strategy
The force on the nail (neglecting the nail's own weight) is the weight of the picture . If we can find , then the mass of the picture is just . The equation can be solved for .
Solution
Solving the equation for , we see that all other quantities can be found:
S is found in [link] and is . The radius is 0.750 mm (as seen in the figure), so the cross-sectional area is
The value for is also shown in the figure. Thus,
This 51 N force is the weight of the picture, so the picture's mass is
Discussion
This is a fairly massive picture, and it is impressive that the nail flexes only —an amount undetectable to the unaided eye.
An object will be compressed in all directions if inward forces are applied evenly on all its surfaces as in [link] . It is relatively easy to compress gases and extremely difficult to compress liquids and solids. For example, air in a wine bottle is compressed when it is corked. But if you try corking a brim-full bottle, you cannot compress the wine—some must be removed if the cork is to be inserted. The reason for these different compressibilities is that atoms and molecules are separated by large empty spaces in gases but packed close together in liquids and solids. To compress a gas, you must force its atoms and molecules closer together. To compress liquids and solids, you must actually compress their atoms and molecules, and very strong electromagnetic forces in them oppose this compression.
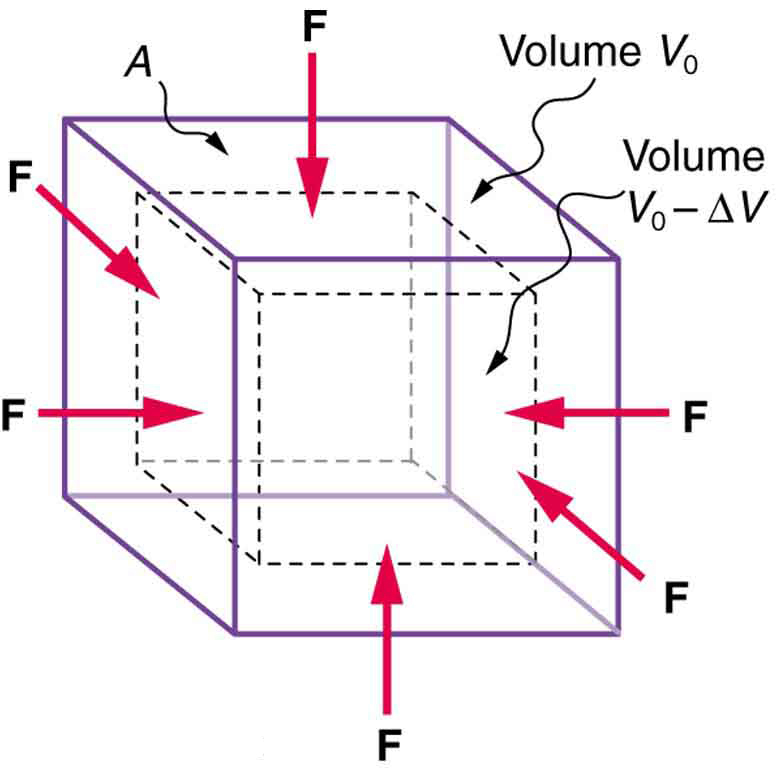
We can describe the compression or volume deformation of an object with an equation. First, we note that a force “applied evenly” is defined to have the same stress, or ratio of force to area on all surfaces. The deformation produced is a change in volume , which is found to behave very similarly to the shear, tension, and compression previously discussed. (This is not surprising, since a compression of the entire object is equivalent to compressing each of its three dimensions.) The relationship of the change in volume to other physical quantities is given by

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?