| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
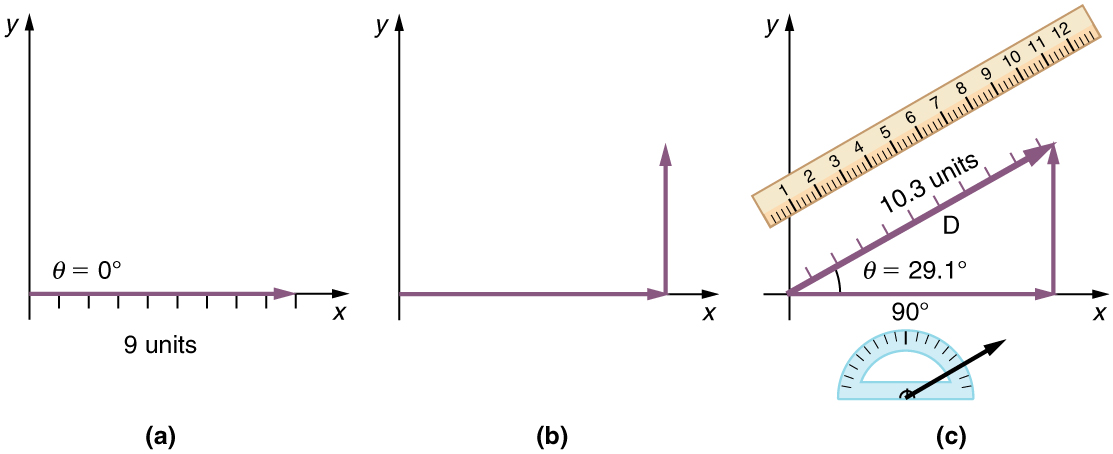
Step 1. Draw an arrow to represent the first vector (9 blocks to the east) using a ruler and protractor .

Step 2. Now draw an arrow to represent the second vector (5 blocks to the north). Place the tail of the second vector at the head of the first vector .
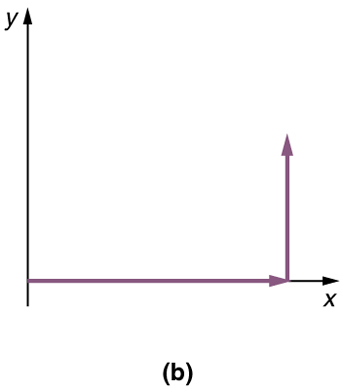
Step 3. If there are more than two vectors, continue this process for each vector to be added. Note that in our example, we have only two vectors, so we have finished placing arrows tip to tail .
Step 4. Draw an arrow from the tail of the first vector to the head of the last vector . This is the resultant , or the sum, of the other vectors.
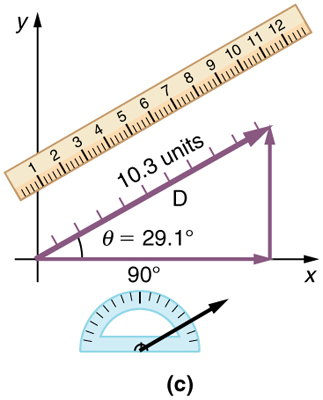
Step 5. To get the magnitude of the resultant, measure its length with a ruler. (Note that in most calculations, we will use the Pythagorean theorem to determine this length.)
Step 6. To get the direction of the resultant, measure the angle it makes with the reference frame using a protractor. (Note that in most calculations, we will use trigonometric relationships to determine this angle.)
The graphical addition of vectors is limited in accuracy only by the precision with which the drawings can be made and the precision of the measuring tools. It is valid for any number of vectors.
Use the graphical technique for adding vectors to find the total displacement of a person who walks the following three paths (displacements) on a flat field. First, she walks 25.0 m in a direction north of east. Then, she walks 23.0 m heading north of east. Finally, she turns and walks 32.0 m in a direction 68.0° south of east.
Strategy
Represent each displacement vector graphically with an arrow, labeling the first , the second , and the third , making the lengths proportional to the distance and the directions as specified relative to an east-west line. The head-to-tail method outlined above will give a way to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant displacement, denoted .
Solution
(1) Draw the three displacement vectors.
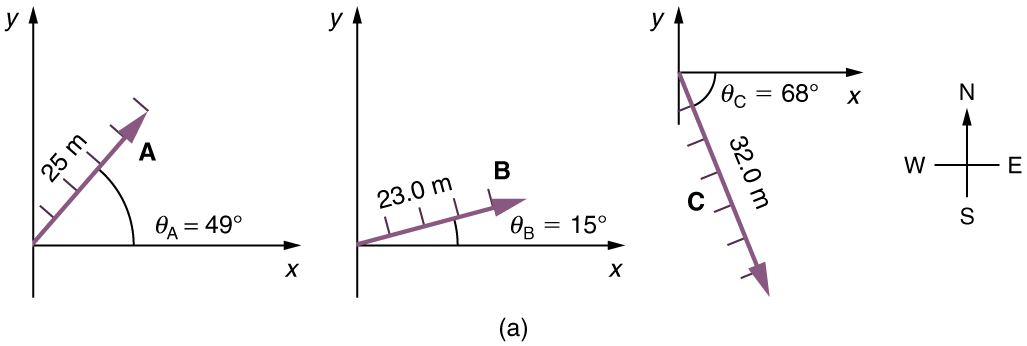
(2) Place the vectors head to tail retaining both their initial magnitude and direction.

(3) Draw the resultant vector, .
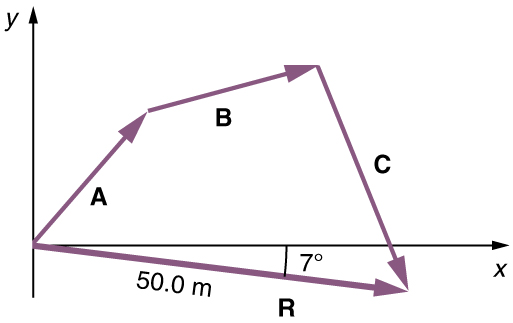
(4) Use a ruler to measure the magnitude of , and a protractor to measure the direction of . While the direction of the vector can be specified in many ways, the easiest way is to measure the angle between the vector and the nearest horizontal or vertical axis. Since the resultant vector is south of the eastward pointing axis, we flip the protractor upside down and measure the angle between the eastward axis and the vector.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?