| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Motors are the most common application of magnetic force on current-carrying wires. Motors have loops of wire in a magnetic field. When current is passed through the loops, the magnetic field exerts force on the loops, which rotates a shaft. Electrical energy is converted to mechanical work in the process. (See [link] .)
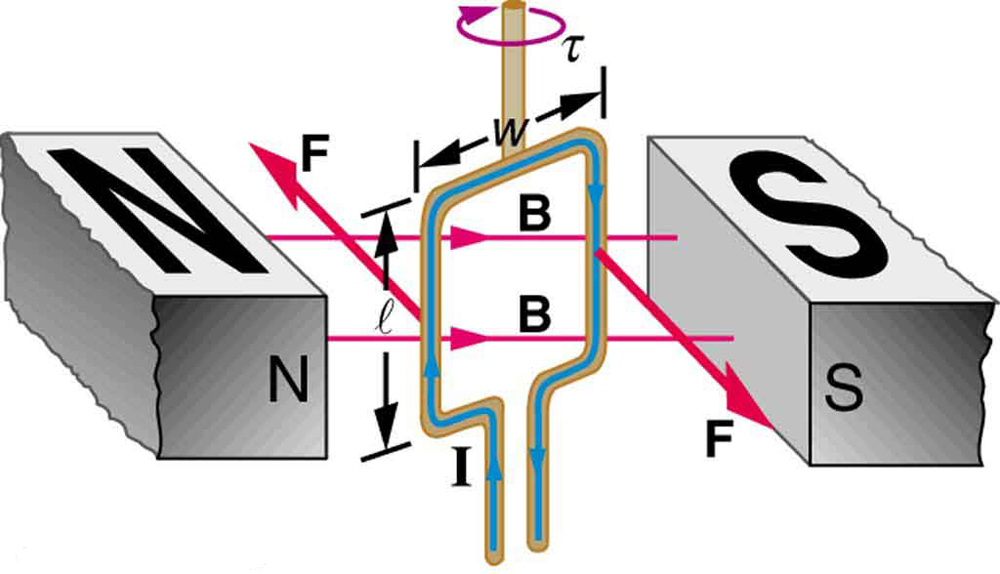
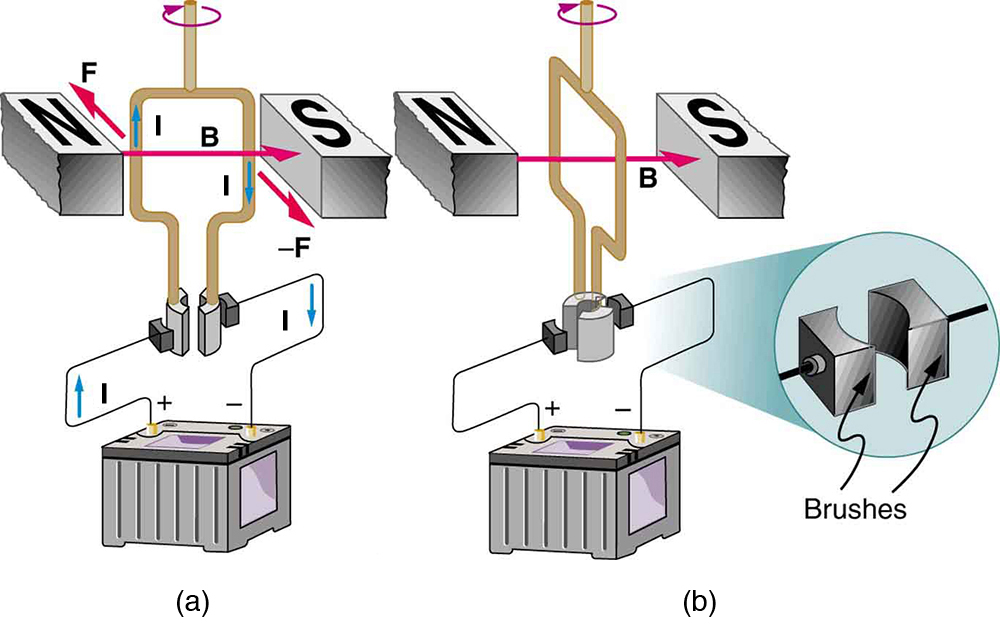
As the coil rotates, the force decreases to zero at . The force then reverses its direction once the coil rotates past . This means that, unless we do something, the coil will oscillate back and forth about equilibrium at . To get the coil to continue rotating in the same direction, we can reverse the current as it passes through with automatic switches called brushes . (See [link] .)
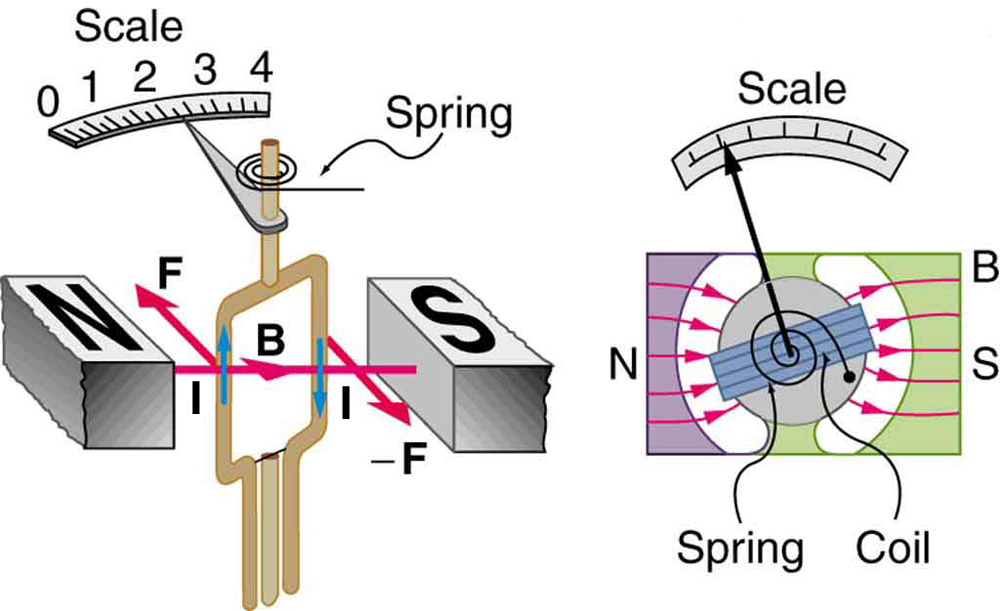
Meters , such as those in analog fuel gauges on a car, are another common application of magnetic force on a current-carrying loop. [link] shows that a meter is very similar in construction to a motor. The meter in the figure has its magnets shaped to limit the effect of by making perpendicular to the loop over a large angular range. A linear spring exerts a counter-force that balances the current-produced force. This makes the needle deflection proportional to . If an exact proportionality cannot be achieved, the gauge reading can be calibrated. To produce a galvanometer for use in analog voltmeters and ammeters that have a low resistance and respond to small currents, we use a large loop area , high magnetic field , and low-resistance coils.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of physics' conversation and receive update notifications?