| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
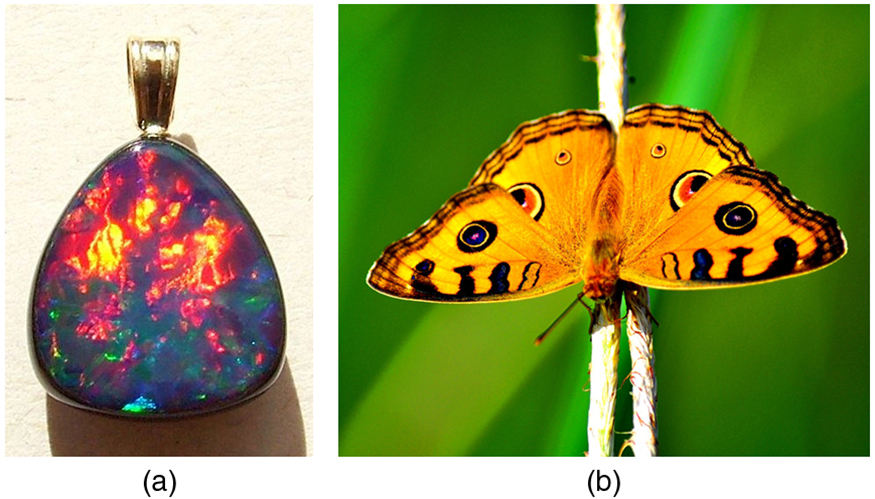
An interesting thing happens if you pass light through a large number of evenly spaced parallel slits, called a diffraction grating . An interference pattern is created that is very similar to the one formed by a double slit (see [link] ). A diffraction grating can be manufactured by scratching glass with a sharp tool in a number of precisely positioned parallel lines, with the untouched regions acting like slits. These can be photographically mass produced rather cheaply. Diffraction gratings work both for transmission of light, as in [link] , and for reflection of light, as on butterfly wings and the Australian opal in [link] or the CD pictured in the opening photograph of this chapter, [link] . In addition to their use as novelty items, diffraction gratings are commonly used for spectroscopic dispersion and analysis of light. What makes them particularly useful is the fact that they form a sharper pattern than double slits do. That is, their bright regions are narrower and brighter, while their dark regions are darker. [link] shows idealized graphs demonstrating the sharper pattern. Natural diffraction gratings occur in the feathers of certain birds. Tiny, finger-like structures in regular patterns act as reflection gratings, producing constructive interference that gives the feathers colors not solely due to their pigmentation. This is called iridescence.

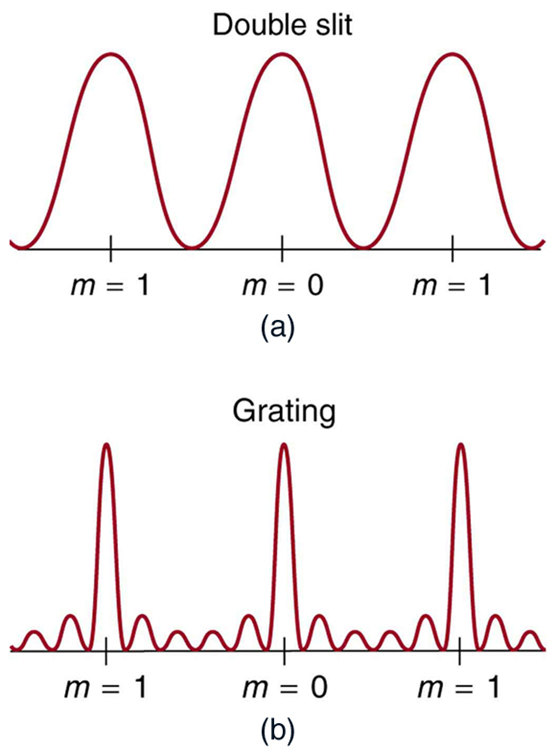
The analysis of a diffraction grating is very similar to that for a double slit (see [link] ). As we know from our discussion of double slits in Young's Double Slit Experiment , light is diffracted by each slit and spreads out after passing through. Rays traveling in the same direction (at an angle relative to the incident direction) are shown in the figure. Each of these rays travels a different distance to a common point on a screen far away. The rays start in phase, and they can be in or out of phase when they reach a screen, depending on the difference in the path lengths traveled. As seen in the figure, each ray travels a distance different from that of its neighbor, where is the distance between slits. If this distance equals an integral number of wavelengths, the rays all arrive in phase, and constructive interference (a maximum) is obtained. Thus, the condition necessary to obtain constructive interference for a diffraction grating is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Yupparaj english program physics corresponding to thai physics book #3' conversation and receive update notifications?