| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
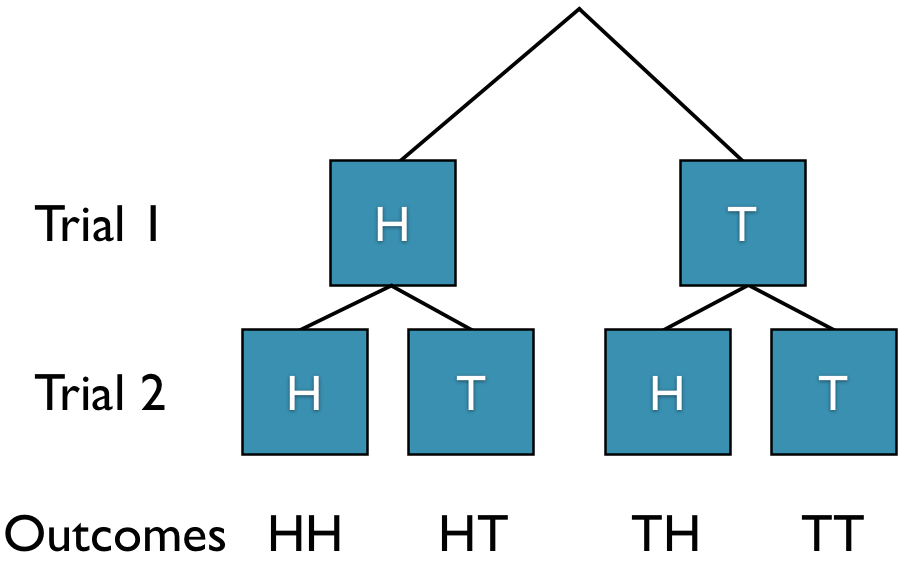
Instead of writing out all possible outcomes for an experiment, we can quickly find the total number of possible outcomes. We have already discussed that when tossing a coin twice, there are two trials which result in 4 different outcomes (S = {HH, HT, TH, TT}). We can use a tree diagram to represent this in the figure below.
For tossing the coin 3 times, we get 8 possible outcomes S = { HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT, THH, THT, TTH, TTT }. The tree diagram is displayed below.
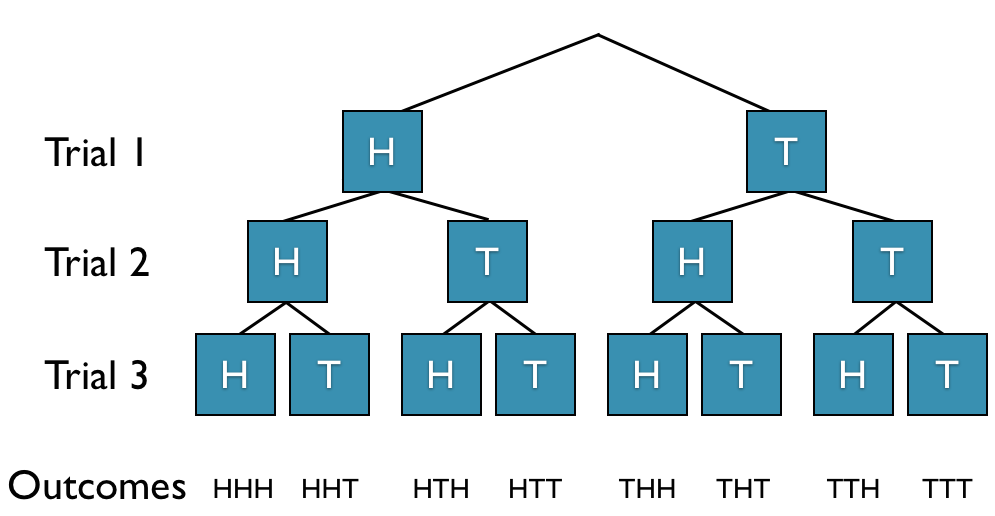
From the tree diagram we can see that the number of outcomes increases by a factor of 2 with each trial.
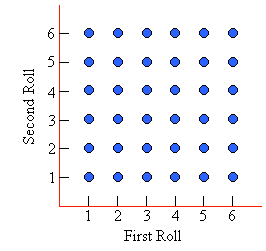
A die is rolled twice.
possible outcomes

A quick way to get the total number of possible outcomes without writing out the sample space or creating a visual aid is to multiply the number of possible outcomes for each trial.
When tossing a coin twice, there are two possible outcomes for each trial (H,T) regardless of whether the coin is weighted or not. If we multiply the two outcomes for the first trial and the two outcomes for the second trial we get possible outcomes. S = { HH, HT, TH, TT }.
When tossing a coin three times, there are two possible outcomes for each trial (H,T) and we end up with 8 possible outcomes. From the tree diagram we saw that we get S = { HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT, THH, THT, TTH, TTT }.
We can extend this concept to tossing a coin 4 times where there are 16 possible outcomes. We will leave it up to you to write out the sample space.
You are going to toss a coin and roll a die.
Suppose we wish to arrange four pictures in a row along a wall. How many different outcomes are possible?
There are four pictures that can be selected for the first position on the wall. If we choose one picture to hang first, we are now left with three choices of pictures for the next position on the wall. Using the multiplicative rule, there are possible arrangements of pictures for the first two positions on the wall. If we continue with this procedure, we now only have two pictures to choose from for the third position and the last picture goes in the last position. As a result, there are 24 possible arrangements of the pictures in a row along a wall.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introduction to statistics i - stat 213 - university of calgary - ver2015revb' conversation and receive update notifications?