| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Most people are familiar with carbohydrates, one type of macromolecule, especially when it comes to what we eat. To lose weight, some individuals adhere to “low-carb” diets. Athletes, in contrast, often “carb-load” before important competitions to ensure that they have enough energy to compete at a high level. Carbohydrates are, in fact, an essential part of our diet; grains, fruits, and vegetables are all natural sources of carbohydrates. Carbohydrates provide energy to the body, particularly through glucose, a simple sugar that is a component of starch and an ingredient in many staple foods. Carbohydrates also have other important functions in humans, animals, and plants.
Carbohydrates are classified into three subtypes: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
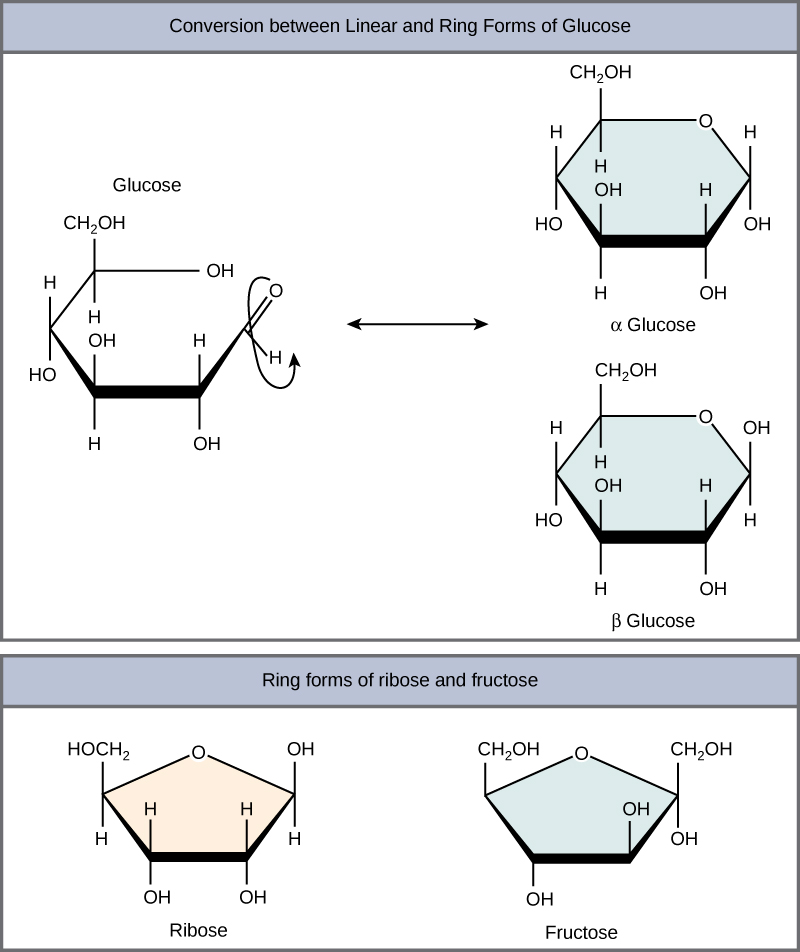
Monosaccharides (mono- = “one”; sacchar- = “sweet”) are simple sugars, the most common of which is glucose. Most monosaccharide names end with the suffix -ose. Monosaccharides can exist as a linear chain or as ring-shaped molecules.
The chemical formula for glucose is C 6 H 12 O 6 . In humans, glucose is an important source of energy. During cellular respiration, energy is released from glucose, and that energy is used to help make adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Plants synthesize glucose using carbon dioxide and water, and glucose in turn is used for energy requirements for the plant. Excess glucose is often stored as starch that is catabolized (the breakdown of larger molecules by cells) by humans and other animals that feed on plants.
Galactose (part of lactose, or milk sugar) and fructose (found in sucrose, in fruit) are other common monosaccharides. Although glucose, galactose, and fructose all have the same chemical formula (C 6 H 12 O 6 ), they differ structurally and chemically (and are known as isomers) because of the different arrangement of functional groups around the asymmetric carbon; all of these monosaccharides have more than one asymmetric carbon ( [link] ).
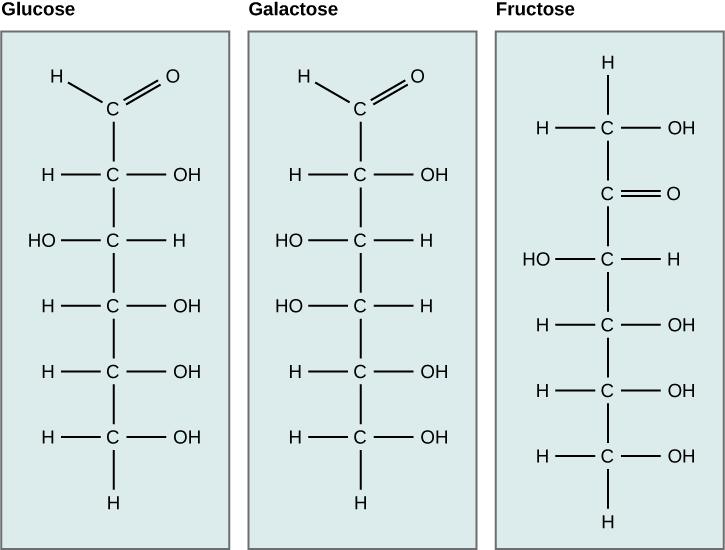
What kind of sugars are these, aldose or ketose?
Disaccharides (di- = “two”) form when two monosaccharides undergo a dehydration reaction (also known as a condensation reaction or dehydration synthesis). During this process, the hydroxyl group of one monosaccharide combines with the hydrogen of another monosaccharide, releasing a molecule of water and forming a covalent bond.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'General biology part i - mixed majors' conversation and receive update notifications?