| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Deuterostomes include the phyla Echinodermata and Chordata (which includes the vertebrates) and two smaller phyla. Deuterostomes share similar patterns of early development.
Echinodermata are named for their spiny skin (from the Greek “echinos” meaning “spiny” and “dermos” meaning “skin”). The phylum includes about 7,000 “Number of Living Species in Australia and the World,” A.D. Chapman, Australia Biodiversity Information Services, last modified August 26, 2010, http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/abrs/publications/other/species-numbers/2009/03-exec-summary.html. described living species, such as sea stars, sea cucumbers, sea urchins, sand dollars, and brittle stars. Echinodermata are exclusively marine.
Adult echinoderms exhibit pentaradial symmetry and have a calcareous endoskeleton made of ossicles ( [link] ), although the early larval stages of all echinoderms have bilateral symmetry. The endoskeleton is developed by epidermal cells, which may also possess pigment cells, giving vivid colors to these animals, as well as cells laden with toxins. These animals have a true coelom, a portion of which is modified into a unique circulatory system called a water vascular system . An interesting feature of these animals is their power to regenerate, even when over 75 percent of their body mass is lost.
Echinoderms have a unique system for gas exchange, nutrient circulation, and locomotion called the water vascular system. The system consists of a central ring canal and radial canals extending along each arm. Water circulates through these structures allowing for gas, nutrient, and waste exchange. A structure on top of the body, called the madreporite , regulates the amount of water in the water vascular system. “Tube feet,” which protrude through openings in the endoskeleton, may be expanded or contracted using the hydrostatic pressure in the system. The system allows for slow movement, but a great deal of power, as witnessed when the tube feet latch on to opposite halves of a bivalve mollusk, like a clam, and slowly, but surely pull the shells apart, exposing the flesh within.
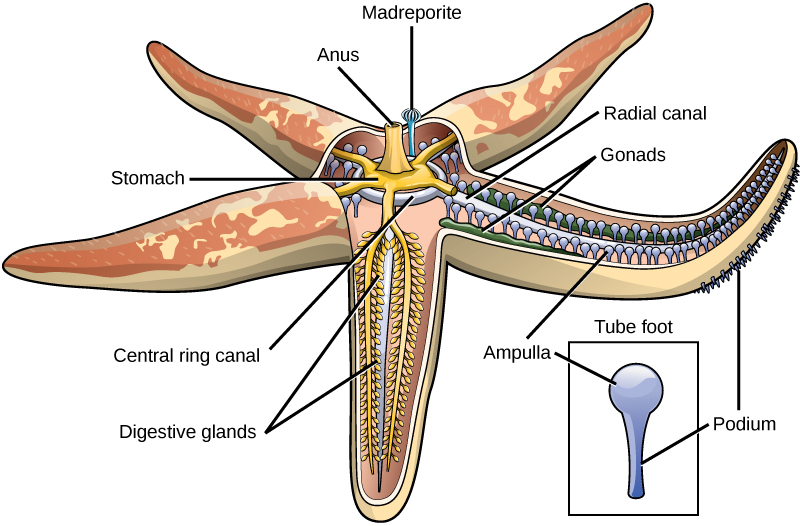
The echinoderm nervous system has a nerve ring at the center and five radial nerves extending outward along the arms. There is no centralized nervous control. Echinoderms have separate sexes and release their gametes into the water where fertilization takes place. Echinoderms may also reproduce asexually through regeneration from body parts.
This phylum is divided into five classes: Asteroidea (sea stars), Ophiuroidea (brittle stars), Echinoidea (sea urchins and sand dollars), Crinoidea (sea lilies or feather stars), and Holothuroidea (sea cucumbers) ( [link] ).
Perhaps the best-known echinoderms are members of the class Asteroidea, or sea stars. They come in a large variety of shapes, colors, and sizes, with more than 1,800 species known. The characteristics of sea stars that set them apart from other echinoderm classes include thick arms that extend from a central disk where organs penetrate into the arms. Sea stars use their tube feet not only for gripping surfaces but also for grasping prey. Sea stars have two stomachs, one of which they can evert through their mouths to secrete digestive juices into or onto prey before ingestion. This process can essentially liquefy the prey and make digestion easier.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bmcc 103 - concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?