| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
1. The occurrence and causes of volcanoes
Molten rock below the earth’s crust is called magma. When it flows to the surface it is called lava. Why lava flows to the surface is not clear enough for people to agree on the reasons for eruptions and no one has been able to investigate the heart of the earth to find out what happens there.
We do know, however, that the weight of the solid crust of the earth is so great that the fluid rock is forced upwards at weak places in the earth’s crust. This molten rock is extremely hot, with temperatures of between 800 and 1 500 C.
If you shake a can of cooldrink, the gas will propel the cooldrink out of the can with great force when you open the can. This is what happens in the case of volcanoes – the molten rock erupts through weak places in the earth’s crust and lava, rocks and ash are propelled into the air.
Then the lava cools down and solidifies to form new rocks known as igneous rock.
Some volcanoes produce very fluid lava that flows over a large area before solidifying. Thin plates of igneous rock are formed in this case. Other volcanoes build up domes because the lava is less fluid and does not flow far from the core.
A very forceful explosion can force out the whole of the dome and cause a large open hole called a caldera, or crater. There are roughly 450 active volcanoes worldwide. Fortunately, they do not erupt continuously and are therefore referred to as dormant volcanoes.


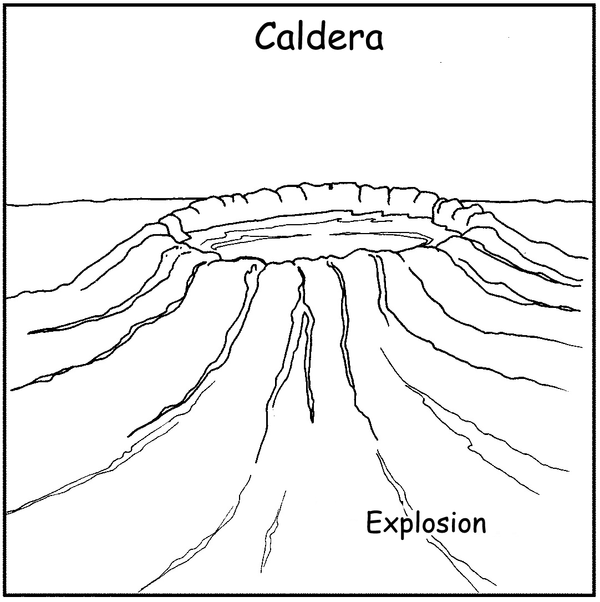
Study figure 4.
There are about 5 000 volcanoes. They only occur in particular places. These places are situated above the margins of the large plates of the earth’s crust. The movement of these plates lead to volcanic eruptions and earthquakes.
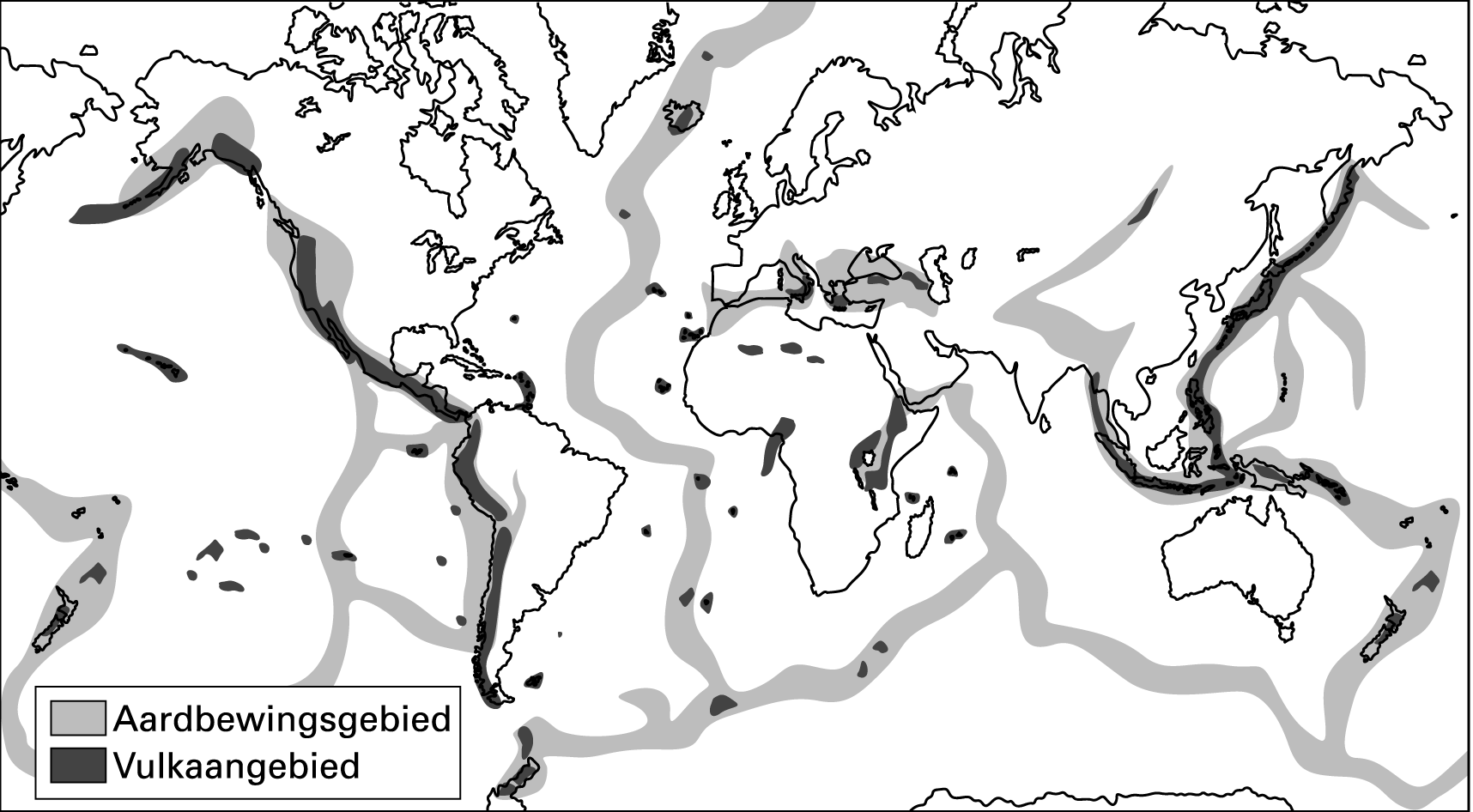
Quake areasVolcanic areas
Figure 4
The distribution of the main volcanic and earthquake areas of the earth
Which volcanoes have caused the greatest destruction?
The most destructive volcano of all time was Krakatoa, in Indonesia. When it erupted in 1883, more than 36 000 people died. The bang of the explosion was heard 5 000 km away and the pollution that resulted from the eruption was visible in copper-coloured sunsets across the earth for years.
Another well-known example of the destructive force of a volcano comes from the eruption of Mount Vesuvius, which buried the city of Pompeii in the Bay of Naples under volcanic rocks and ashes in 79 AD.
2. The effect (consequences) of volcanoes on people’s lives and their socio-economic activities
Thousands of lights glitter in the dark dome of the night. From a distance the explosions that hurtle glowing rocks and streams of fire into the night look like an expansive display of fireworks. Rocks and ashes flung up high pollute the air.
A river of red, smoking lava slithers over the edge of the crater – the warm blood of the living earth, as someone has strikingly described it.
It may flow through fertile valleys for kilometres, devouring every blade of grass, even trees, along its way. Houses crumble and cities are buried under the glowing, driven mass. People who have survived, scramble down the mountainside; warm ash raining down on them. Suffocating sulphurous gases and a rain of ashes smother other people to death.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Geography grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?