| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
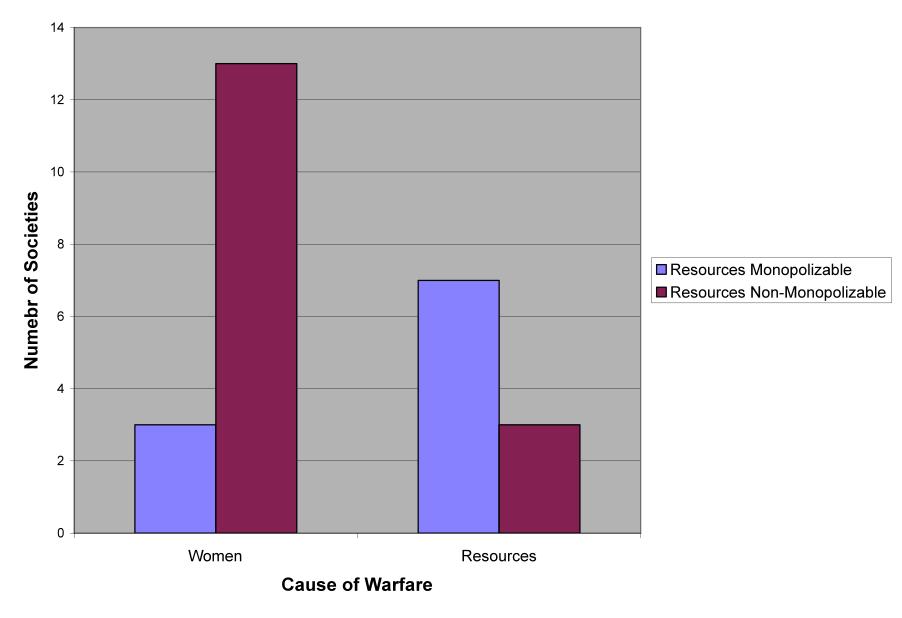
The relationship between polygyny and ability to monopolize resources. (data adapted from manson and wrangham 1991)
The patterns of availability of resources also appear to correlate with occurrences of warfare. Outbreaks of war correlate with food shortages; war prevalence also correlates with the threat of food shortages or resource-depleting natural disasters (Ember and Ember 1992). In contrast, more peaceful interactions would be favored in conditions where resource supply is sufficient to exceed demand, groups are unlikely to come into contact with each other frequently, or an alternate resource is available to fulfill the same purpose (Durham 1976). Additionally, in regions where resources are generally very scarce, and availability differs between regions over time so that groups are forced to migrate in order to survive, cooperation with out-groups is favored over aggressive interactions. For example, Eskimos in more arctic areas migrate with the game, and seldom engage in aggressive behavior with passing neighbors. Groups that reside further south in areas which have a more consistent supply of game are far more likely to engage in violent conflict (Durham 1976).
However, in order for the aggressor to gain in fitness and outweigh the costs of violent behavior, the resource must sufficiently contribute to an increase in fitness, while the aggressor also must be sufficiently likely to defeat the competitor without suffering overwhelming reproductive costs (Durham 1976). Expanding upon this hypothesis, individuals would gain from joining groups to commit acts of aggression either in situations where the aggressive individuals themselves have access to the acquired resource sufficient to outweigh the potential fitness costs, while those who did not participate in the collective aggression do not benefit from increased access to the resource, or alternatively in situations where the aggressive individuals do not necessarily have direct access to the acquired resource, but do enjoy some other form of benefit from within the group sufficient to outweigh the fitness costs.
| Factors contributing to Fitness Benefit | Factors contributing to Fitness Cost |
| Quality of resource | Size of competitors |
| Availability of resource over time | Strength of competitors |
| Distribution of resource in space | Technological state of competitor weapons |
| Possible uses of resource |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mockingbird tales: readings in animal behavior' conversation and receive update notifications?