| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
CHẤT BÁN DẪN ĐIỆN THUẦN HAY NỘI BẨM:(Pure semiconductor or intrinsic semiconductor)
Hầu hết các chất bán dẫn đều có các nguyên tử sắp xếp theo cấu tạo tinh thể. Hai chất bán dẫn được dùng nhiều nhất trong kỹ thuật chế tạo linh kiện điện tử là Silicium và Germanium. Mỗi nguyên tử của hai chất này đều có 4 điện tử ở ngoài cùng kết hợp với 4 điện tử của 4 nguyên tử kế cận tạo thành 4 liên kết hóa trị. Vì vậy tinh thể Ge và Si ở nhiệt độ thấp là các chất cách điện.

Nếu ta tăng nhiệt độ tinh thể, nhiệt năng sẽ làm tăng năng lượng một số điện tử và làm gãy một số nối hóa trị. Các điện tử ở các nối bị gãy rời xa nhau và có thể di chuyển dễ dàng trong mạng tinh thể dưới tác dụng của điện trường. Tại các nối hóa trị bị gãy ta có các lỗ trống (hole). Về phương diện năng lượng, ta có thể nói rằng nhiệt năng làm tăng năng lượng các điện tử trong dải hóa trị.
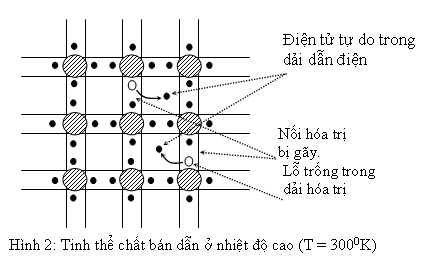
Khi năng lượng này lớn hơn năng lượng của dải cấm (0,7eV đối với Ge và 1,12eV đối với Si), điện tử có thể vượt dải cấm vào dải dẫn điện và chừa lại những lỗ trống (trạng thái năng lượng trống) trong dải hóa trị). Ta nhận thấy số điện tử trong dải dẫn điện bằng số lỗ trống trong dải hóa trị.
Nếu ta gọi n là mật độ điện tử có năng lượng trong dải dẫn điện và p là mật độ lỗ trống có năng lượng trong dải hóa trị. Ta có:n=p=ni
Người ta chứng minh được rằng:
ni2 = A0.T3. exp(-EG/KT)
Trong đó: A0 : Số Avogadro=6,203.1023
T : Nhiệt độ tuyệt đối (Độ Kelvin)
K : Hằng số Bolzman=8,62.10-5 eV/0K
EG : Chiều cao của dải cấm.

Ta gọi chất bán dẫn có tính chất n=p là chất bán dẫn nội bẩm hay chất bán dẫn thuần. Thông thường người ta gặp nhiều khó khăn để chế tạo chất bán dẫn loại này.
Giả sử ta pha vào Si thuần những nguyên tử thuộc nhóm V của bảng phân loại tuần hoàn như As (Arsenic), Photpho (p), Antimony (Sb). Bán kính nguyên tử của As gần bằng bán kính nguyên tử của Si nên có thể thay thế một nguyên tử Si trong mạng tinh thể. Bốn điện tử của As kết hợp với 4 điện tử của Si lân cận tạo thành 4 nối hóa trị, Còn dư lại một điện tử của As. Ở nhiệt độ thấp, tất cả các điện tử của các nối hóa trị đều có năng lượng trong dải hóa trị, trừ những điện tử thừa của As không tạo nối hóa trị có năng lượng ED nằm trong dải cấm và cách dẫy dẫn điện một khỏang năng lượng nhỏ chừng 0,05eV.
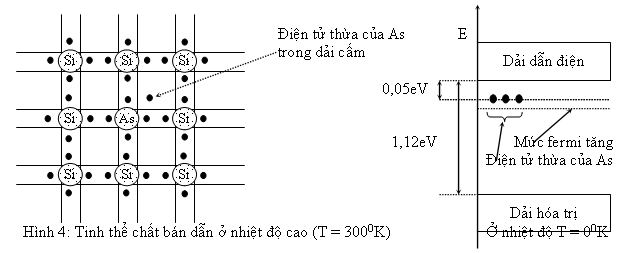
Giả sử ta tăng nhiệt độ của tinh thể, một số nối hóa trị bị gãy, ta có những lỗ trống trong dải hóa trị và những điện tử trong dải dẫn điện giống như trong trường hợp của các chất bán dẫn thuần. Ngoài ra, các điện tử của As có năng lượng ED cũng nhận nhiệt năng để trở thành những điện tử có năng lượng trong dải dẫn điện. Vì thế ta có thể coi như hầu hết các nguyên tử As đều bị Ion hóa (vì khỏang năng lượng giữa ED và dải dẫn điện rất nhỏ), nghĩa là tất cả các điện tử lúc đầu có năng lượng ED đều được tăng năng lượng để trở thành điện tử tự do.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Điện tử ứng dụng' conversation and receive update notifications?