| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
This chapter will focus on the electromagnetic (EM) radiation. Electromagnetic radiation is a self-propagating wave in space with electric and magnetic components. These components oscillate at right angles to each other and to the direction of propagation, and are in phase with each other. Electromagnetic radiation is classified into types according to the frequency of the wave: these types include, in order of increasing frequency, radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays.
If you watch a colony of ants walking up the wall, they look like a thin continuous black line. But as you look closer, you see that the line is made up of thousands of separated black ants.
Light and all other types of electromagnetic radiation seems like a continuous wave at first, but when one performs experiments with light, one can notice that light can have both wave and particle like properties. Just like the individual ants, the light can also be made up of individual bundles of energy, or quanta of light.
Light has both wave-like and particle-like properties (wave–particle duality), but only shows one or the other, depending on the kind of experiment we perform. A wave-type experiment shows the wave nature, and a particle-type experiment shows particle nature. One cannot test the wave and the particle nature at the same time. A particle of light is called a photon.
A photon is a quantum (energy packet) of light.
The particle nature of light can be demonstrated by the interaction of photons with matter. One way in which light interacts with matter is via the photoelectric effect, which will be studied in detail in [link] .
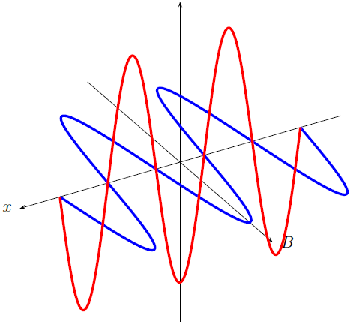
Accelerating charges emit electromagnetic waves. We have seen that a changing electric field generates a magnetic field and a changing magnetic field generates an electric field. This is the principle behind the propagation of electromagnetic waves, because electromagnetic waves, unlike sound waves, do not need a medium to travel through. EM waves propagate when an electric field oscillating in one plane produces a magnetic field oscillating in a plane at right angles to it, which produces an oscillating electric field, and so on. The propagation of electromagnetic waves can be described as mutual induction .
These mutually regenerating fields travel through empty space at a constant speed of , represented by .

Observe the things around you, your friend sitting next to you, a large tree across the field. How is it that you are able to see these things? What is it that is leaving your friend's arm and entering your eye so that you can see his arm? It is light. The light originally comes from the sun, or possibly a light bulb or burning fire. In physics, light is given the more technical term electromagnetic radiation, which includes all forms of light, not just the form which you can see with your eyes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Maths test' conversation and receive update notifications?