| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
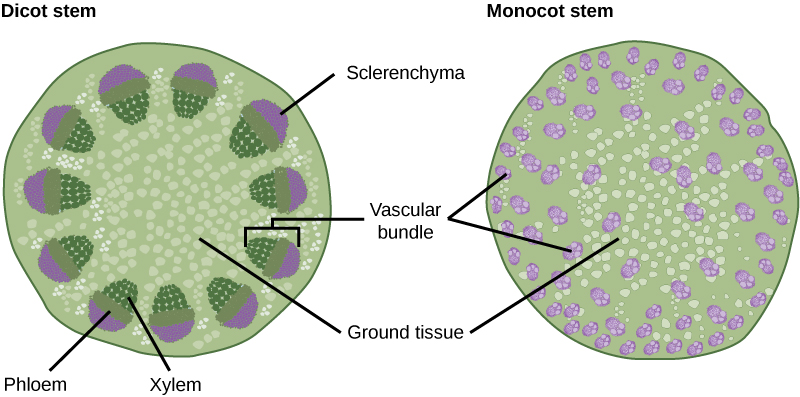
The xylem and phloem that make up the vascular tissue of the stem are arranged in distinct strands called vascular bundles, which run up and down the length of the stem. When the stem is viewed in cross section, the vascular bundles of dicot stems are arranged in a ring. In plants with stems that live for more than one year, the individual bundles grow together and produce the characteristic growth rings. In monocot stems, the vascular bundles are randomly scattered throughout the ground tissue ( [link] ).
Xylem tissue has three types of cells: xylem parenchyma, tracheids, and vessel elements. The latter two types conduct water and are dead at maturity. Tracheids are xylem cells with thick secondary cell walls that are lignified. Water moves from one tracheid to another through regions on the side walls known as pits, where secondary walls are absent. Vessel elements are xylem cells with thinner walls; they are shorter than tracheids. Each vessel element is connected to the next by means of a perforation plate at the end walls of the element. Water moves through the perforation plates to travel up the plant.
Phloem tissue is composed of sieve-tube cells, companion cells, phloem parenchyma, and phloem fibers. A series of sieve-tube cells (also called sieve-tube elements) are arranged end to end to make up a long sieve tube, which transports organic substances such as sugars and amino acids. The sugars flow from one sieve-tube cell to the next through perforated sieve plates, which are found at the end junctions between two cells. Although still alive at maturity, the nucleus and other cell components of the sieve-tube cells have disintegrated. Companion cells are found alongside the sieve-tube cells, providing them with metabolic support. The companion cells contain more ribosomes and mitochondria than the sieve-tube cells, which lack some cellular organelles.
Ground tissue is mostly made up of parenchyma cells, but may also contain collenchyma and sclerenchyma cells that help support the stem. The ground tissue towards the interior of the vascular tissue in a stem or root is known as pith , while the layer of tissue between the vascular tissue and the epidermis is known as the cortex .
Growth in plants occurs as the stems and roots lengthen. Some plants, especially those that are woody, also increase in thickness during their life span. The increase in length of the shoot and the root is referred to as primary growth , and is the result of cell division in the shoot apical meristem. Secondary growth is characterized by an increase in thickness or girth of the plant, and is caused by cell division in the lateral meristem. [link] shows the areas of primary and secondary growth in a plant. Herbaceous plants mostly undergo primary growth, with hardly any secondary growth or increase in thickness. Secondary growth or “wood” is noticeable in woody plants; it occurs in some dicots, but occurs very rarely in monocots.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bio 351 university of texas' conversation and receive update notifications?