| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
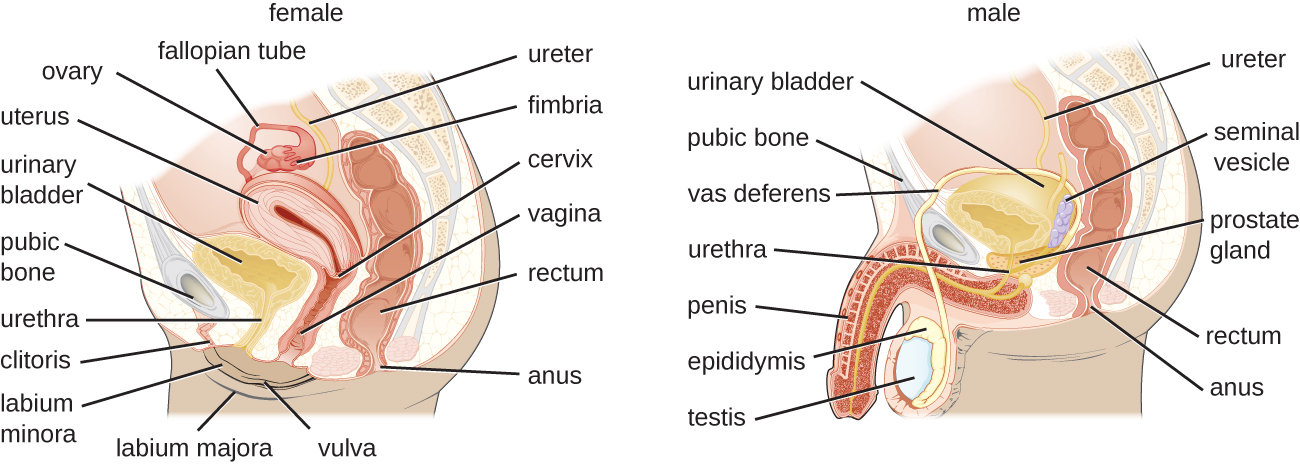
The male reproductive system ( [link] ) is located in close proximity to the urinary system, and the urethra is part of both systems. The testes are responsible for the production of sperm. The epididymis is a coiled tube that collects sperm from the testes and passes it on to the vas deferens. The epididymis is also the site of sperm maturation after they leave the testes. The seminal vesicles and prostate are accessory glands that produce fluid that supports sperm. During ejaculation, the vas deferens releases this mixture of fluid and sperm, called semen, into the urethra, which extends to the end of the penis .
The female reproductive system is located near the urinary system ( [link] ). The external genitalia ( vulva ) in females open to the vagina , a muscular passageway that connects to the cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus (the organ where a fertilized egg will implant and develop). The cervix is a common site of infection, especially for viruses that may lead to cervical cancer. The uterus leads to the fallopian tubes and eventually to the ovaries. Ovaries are the site of ova (egg) production, as well as the site of estrogen and progesterone production that are involved in maturation and maintenance of reproductive organs, preparation of the uterus for pregnancy, and regulation of the menstrual cycle.
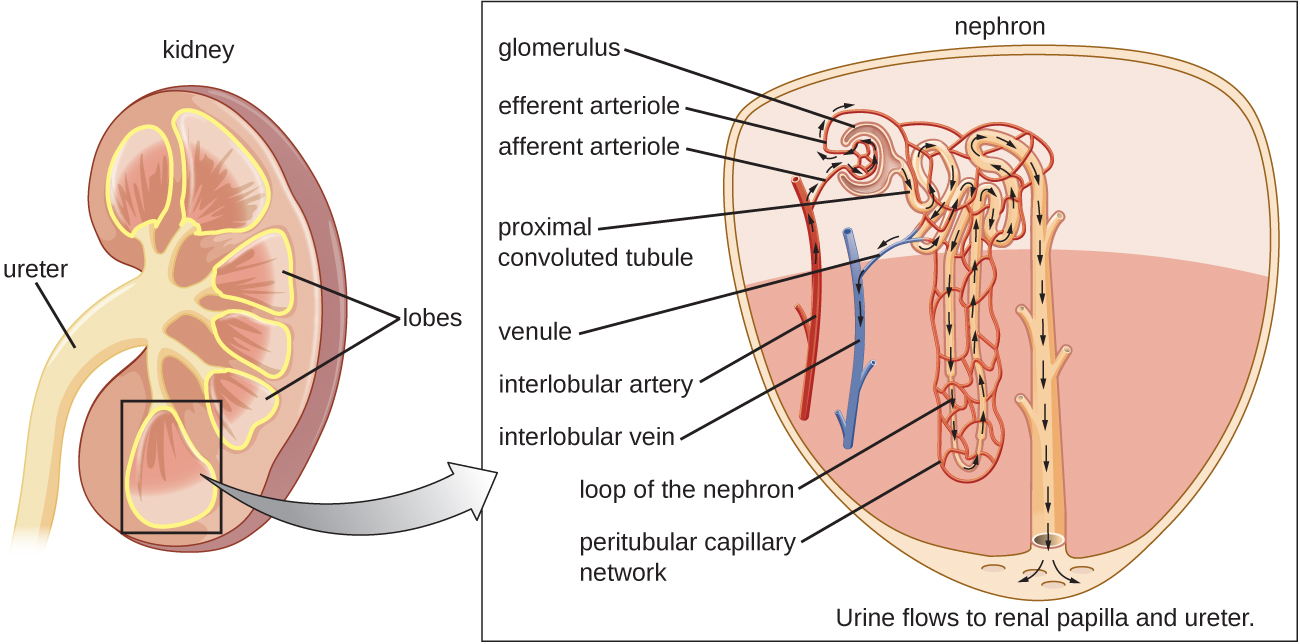
The normal microbiota of different body sites provides an important nonspecific defense against infectious diseases (see Physical Defenses ), and the urogenital tract is no exception. In both men and women, however, the kidneys are sterile. Although urine does contain some antibacterial components, bacteria will grow in urine left out at room temperature. Therefore, it is primarily the flushing action that keeps the ureters and bladder free of microbes.
Below the bladder, the normal microbiota of the male urogenital system is found primarily within the distal urethra and includes bacterial species that are commonly associated with the skin microbiota. In women, the normal microbiota is found within the distal one third of the urethra and the vagina. The normal microbiota of the vagina becomes established shortly after birth and is a complex and dynamic population of bacteria that fluctuates in response to environmental changes. Members of the vaginal microbiota play an important role in the nonspecific defense against vaginal infections and sexually transmitted infections by occupying cellular binding sites and competing for nutrients. In addition, the production of lactic acid by members of the microbiota provides an acidic environment within the vagina that also serves as a defense against infections. For the majority of women, the lactic-acid–producing bacteria in the vagina are dominated by a variety of species of Lactobacillus . For women who lack sufficient lactobacilli in their vagina, lactic acid production comes primarily from other species of bacteria such as Leptotrichia spp., Megasphaera spp., and Atopobium vaginae . Lactobacillus spp. use glycogen from vaginal epithelial cells for metabolism and production of lactic acid. This process is tightly regulated by the hormone estrogen. Increased levels of estrogen correlate with increased levels of vaginal glycogen, increased production of lactic acid, and a lower vaginal pH . Therefore, decreases in estrogen during the menstrual cycle and with menopause are associated with decreased levels of vaginal glycogen and lactic acid, and a higher pH. In addition to producing lactic acid, Lactobacillus spp. also contribute to the defenses against infectious disease through their production of hydrogen peroxide and bacteriocins (antibacterial peptides).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?