| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
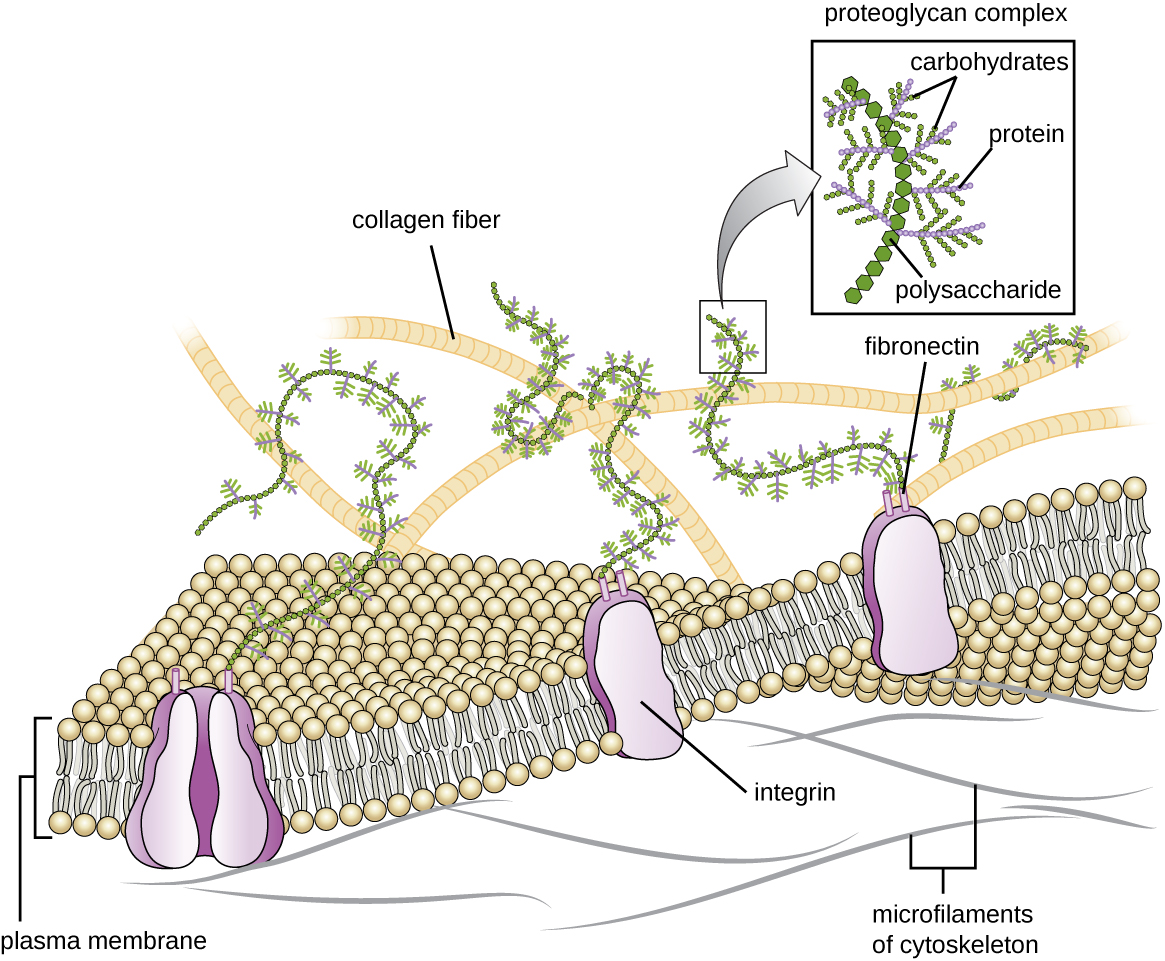
Cells of animals and some protozoans do not have cell walls to help maintain shape and provide structural stability. Instead, these types of eukaryotic cells produce an extracellular matrix for this purpose. They secrete a sticky mass of carbohydrates and proteins into the spaces between adjacent cells ( [link] ). Some protein components assemble into a basement membrane to which the remaining extracellular matrix components adhere. Proteoglycans typically form the bulky mass of the extracellular matrix while fibrous proteins, like collagen , provide strength. Both proteoglycans and collagen are attached to fibronectin proteins, which, in turn, are attached to integrin proteins. These integrin proteins interact with transmembrane proteins in the plasma membranes of eukaryotic cells that lack cell walls.
In animal cells, the extracellular matrix allows cells within tissues to withstand external stresses and transmits signals from the outside of the cell to the inside. The amount of extracellular matrix is quite extensive in various types of connective tissues, and variations in the extracellular matrix can give different types of tissues their distinct properties. In addition, a host cell’s extracellular matrix is often the site where microbial pathogens attach themselves to establish infection. For example, Streptococcus pyogenes , the bacterium that causes strep throat and various other infections, binds to fibronectin in the extracellular matrix of the cells lining the oropharynx (upper region of the throat).
Some eukaryotic cells use flagella for locomotion; however, eukaryotic flagella are structurally distinct from those found in prokaryotic cells. Whereas the prokaryotic flagellum is a stiff, rotating structure, a eukaryotic flagellum is more like a flexible whip composed of nine parallel pairs of microtubules surrounding a central pair of microtubules. This arrangement is referred to as a 9+2 array ( [link] ). The parallel microtubules use dynein motor proteins to move relative to each other, causing the flagellum to bend.
Cilia (singular: cilium ) are a similar external structure found in some eukaryotic cells. Unique to eukaryotes, cilia are shorter than flagella and often cover the entire surface of a cell; however, they are structurally similar to flagella (a 9+2 array of microtubules) and use the same mechanism for movement. A structure called a basal body is found at the base of each cilium and flagellum. The basal body, which attaches the cilium or flagellum to the cell, is composed of an array of triplet microtubules similar to that of a centriole but embedded in the plasma membrane. Because of their shorter length, cilia use a rapid, flexible, waving motion. In addition to motility, cilia may have other functions such as sweeping particles past or into cells. For example, ciliated protozoans use the sweeping of cilia to move food particles into their mouthparts, and ciliated cells in the mammalian respiratory tract beat in synchrony to sweep mucus and debris up and out of the lungs ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?