| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
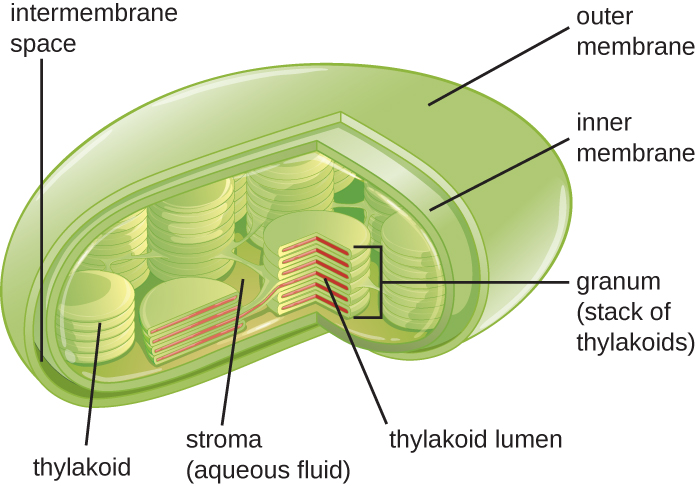
Plant cells and algal cells contain chloroplasts , the organelles in which photosynthesis occurs ( [link] ). All chloroplasts have at least three membrane systems: the outer membrane, the inner membrane, and the thylakoid membrane system. Inside the outer and inner membranes is the chloroplast stroma , a gel-like fluid that makes up much of a chloroplast’s volume, and in which the thylakoid system floats. The thylakoid system is a highly dynamic collection of folded membrane sacs. It is where the green photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll is found and the light reactions of photosynthesis occur. In most plant chloroplasts, the thylakoids are arranged in stacks called grana (singular: granum), whereas in some algal chloroplasts , the thylakoids are free floating.
Other organelles similar to mitochondria have arisen in other types of eukaryotes, but their roles differ. Hydrogenosomes are found in some anaerobic eukaryotes and serve as the location of anaerobic hydrogen production. Hydrogenosomes typically lack their own DNA and ribosomes. Kinetoplasts are a variation of the mitochondria found in some eukaryotic pathogens. In these organisms, each cell has a single, long, branched mitochondrion in which kinetoplast DNA, organized as multiple circular pieces of DNA, is found concentrated at one pole of the cell.
Many protozoans, including several protozoan parasites that cause infections in humans, can be identified by their unusual appearance. Distinguishing features may include complex cell morphologies, the presence of unique organelles, or the absence of common organelles. The protozoan parasites Giardia lamblia and Trichomonas vaginalis are two examples.
G. lamblia , a frequent cause of diarrhea in humans and many other animals, is an anaerobic parasite that possesses two nuclei and several flagella. Its Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum are greatly reduced, and it lacks mitochondria completely. However, it does have organelles known as mitosomes , double-membrane-bound organelles that appear to be severely reduced mitochondria. This has led scientists to believe that G. lamblia’ s ancestors once possessed mitochondria that evolved to become mitosomes. T. vaginalis , which causes the sexually transmitted infection vaginitis, is another protozoan parasite that lacks conventional mitochondria. Instead, it possesses hydrogenosomes , mitochondrial-related, double-membrane-bound organelles that produce molecular hydrogen used in cellular metabolism. Scientists believe that hydrogenosomes, like mitosomes, also evolved from mitochondria. N. Yarlett, J.H.P. Hackstein. “Hydrogenosomes: One Organelle, Multiple Origins.” BioScience 55 no. 8 (2005):657–658.
The plasma membrane of eukaryotic cells is similar in structure to the prokaryotic plasma membrane in that it is composed mainly of phospholipids forming a bilayer with embedded peripheral and integral proteins ( [link] ). These membrane components move within the plane of the membrane according to the fluid mosaic model. However, unlike the prokaryotic membrane, eukaryotic membranes contain sterols , including cholesterol, that alter membrane fluidity. Additionally, many eukaryotic cells contain some specialized lipids, including sphingolipids, which are thought to play a role in maintaining membrane stability as well as being involved in signal transduction pathways and cell-to-cell communication.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?